Estimating the population size of men who have sex with men in the United States to obtain HIV and syphilis rates
- PMID: 23049658
- PMCID: PMC3462414
- DOI: 10.2174/1874613601206010098
Estimating the population size of men who have sex with men in the United States to obtain HIV and syphilis rates
Abstract
Background: CDC has not previously calculated disease rates for men who have sex with men (MSM) because there is no single comprehensive source of data on population size. To inform prevention planning, CDC developed a national population size estimate for MSM to calculate disease metrics for HIV and syphilis.
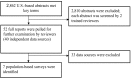
Methods: We conducted a systematic literature search and identified seven surveys that provided data on same-sex behavior in nationally representative samples. Data were pooled by three recall periods and combined using meta-analytic procedures. We applied the proportion of men reporting same-sex behavior in the past 5 years to U.S. census data to produce a population size estimate. We then calculated three disease metrics using CDC HIV and STD surveillance data and rate ratios comparing MSM to other men and to women.
Results: Estimates of the proportion of men who engaged in same-sex behavior differed by recall period: past year = 2.9% (95%CI, 2.6-3.2); past five years = 3.9% (3.5-4.4); ever = 6.9% (5.1-8.6). Rates on all 3 disease metrics were much higher among MSM than among either other men or women (38 to 109 times as high).
Conclusions: Estimating the population size for MSM allowed us to calculate rates for disease metrics and to develop rate ratios showing dramatically higher rates among MSM than among other men or women. These data greatly improve our understanding of the disproportionate impact of these diseases among MSM in the U.S. and help with prevention planning.
Keywords: HIV rates; MSM population size; Prevalence of same-sex behavior among men; syphilis rates..
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance, 2009. Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/std/stats09/default.htm . 2010. [Accessed March 20, 2011].
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV/AIDS Surveillance Report, 2008. vol. 20. Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/topics/surveillance/resources/reports/ 2010. [Accessed February 1, 2011].
-
- Diamond M. Homosexuality and bisexuality in different populations. Arch Sex Behav. 1993;22:291–310. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous