Local delivery of nimodipine by prolonged-release microparticles-feasibility, effectiveness and dose-finding in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage
- PMID: 23049732
- PMCID: PMC3458040
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042597
Local delivery of nimodipine by prolonged-release microparticles-feasibility, effectiveness and dose-finding in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage
Abstract
Background and purpose: To investigate the effect of locally applied nimodipine prolonged-release microparticles on angiographic vasospasm and secondary brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH).
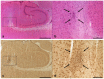
Methods: 70 male Wistar rats were categorized into three groups: 1) sham operated animals (control), 2) animals with SAH only (control) and the 3) treatment group. SAH was induced using the double hemorrhage model. The treatment group received different concentrations (20%, 30% or 40%) of nimodipine microparticles. Angiographic vasospasm was assessed 5 days later using digital subtraction angiography (DSA). Histological analysis of frozen sections was performed using H&E-staining as well as Iba1 and MAP2 immunohistochemistry.
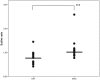
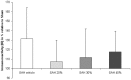
Results: DSA images were sufficient for assessment in 42 animals. Severe angiographic vasospasm was present in group 2 (SAH only), as compared to the sham operated group (p<0.001). Only animals within group 3 and the highest nimodipine microparticles concentration (40%) as well as group 1 (sham) demonstrated the largest intracranial artery diameters. Variation in vessel calibers, however, did not result in differences in Iba-1 or MAP2 expression, i.e. in histological findings for secondary brain injury.
Conclusions: Local delivery of high-dose nimodipine prolonged-release microparticles at high concentration resulted in significant reduction in angiographic vasospasm after experimental SAH and with no histological signs for matrix toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Suarez JI, Tarr RW, Selman WR (2006) Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. N Engl J Med 354: 387–396. - PubMed
-
- Hop JW, Rinkel GJ, Algra A, van Gijn J (1997) Case-fatality rates and functional outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review. Stroke 28: 660–664. - PubMed
-
- Barth M, Capelle HH, Weidauer S, Weiss C, Munch E, et al. (2007) Effect of nicardipine prolonged-release implants on cerebral vasospasm and clinical outcome after severe aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a prospective, randomized, double-blind phase IIa study. Stroke 38: 330–336. - PubMed
-
- Kasuya H, Onda H, Sasahara A, Takeshita M, Hori T (2005) Application of nicardipine prolonged-release implants: analysis of 97 consecutive patients with acute subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 56: 895–902; discussion 895–902. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

