Neuroanatomical characterisation of the expression of the lipodystrophy and motor-neuropathy gene Bscl2 in adult mouse brain
- PMID: 23049863
- PMCID: PMC3458087
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045790
Neuroanatomical characterisation of the expression of the lipodystrophy and motor-neuropathy gene Bscl2 in adult mouse brain
Abstract
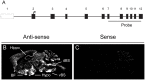
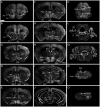
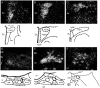
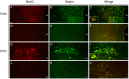
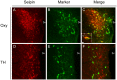
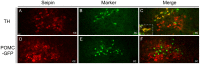
The endoplasmic reticulum localised protein seipin, encoded by the gene Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy type 2 (BSCL2), serves a critical but poorly defined function in the physiology of both adipose and neural tissue. In humans, BSCL2 loss-of-function mutations cause a severe form of lipodystrophy, whilst a distinct set of gain-of-toxic-function mutations are associated with a heterogeneous group of neuropathies. However, despite the importance of seipin dysfunction to the pathophysiology of these conditions, little is known about its physiological role in adipocytes or neurons. BSCL2 mRNA has previously been identified in human and mouse brain, yet no definitive assessment of its expression has been undertaken. Here we comprehensively characterised the neuroanatomical distribution of mouse Bscl2 using complementary in situ hybridisation histochemistry and immunohistochemistry techniques. Whilst Bscl2 was broadly expressed throughout the rostral-caudal extent of the mouse brain, it exhibited a discrete neuroanatomical profile. Bscl2 was most abundantly expressed in the hypothalamus and in particular regions associated with the regulation of energy balance including, the paraventricular, ventromedial, arcuate and dorsomedial nuclei. Bscl2 expression was also identified within the brainstem dorsal vagal complex, which together with the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus represented the site of highest expression. Further neurochemical profiling of these two nuclei revealed Bscl2/seipin expression within energy balance related neuronal populations. Specifically, seipin was detected in oxytocin neurons of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and in catecholamine neurons of the dorsal vagal complex. These data raise the possibility that in addition to its role in adipose tissue development, seipin may also be involved in the central regulation of energy balance.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Fei W, Du X, Yang H (2011) Seipin, adipogenesis and lipid droplets. Trends Endocrinol Metab 22: 204–210. - PubMed
-
- Ito D, Suzuki N (2009) Seipinopathy: a novel endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated disease. Brain 132: 8–15. - PubMed
-
- Rochford JJ (2010) Molecular mechanisms controlling human adipose tissue development: insights from monogenic lipodystrophies. Expert Rev Mol Med 12: e24. - PubMed
-
- Magre J, Delepine M, Khallouf E, Gedde-Dahl T Jr, Van Maldergem L, et al. (2001) Identification of the gene altered in Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy on chromosome 11q13. Nat Genet 28: 365–370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

