Cognition and Hemodynamics
- PMID: 23050027
- PMCID: PMC3462450
- DOI: 10.1007/s12170-012-0260-2
Cognition and Hemodynamics
Abstract
The relationship between cerebral hemodynamics and cognitive performance has increasingly become recognized as a major challenge in clinical practice for older adults. Both diabetes and hypertension worsen brain perfusion and are major risk factors for cerebrovascular disease, stroke and dementia. Cerebrovascular reserve has emerged as a potential biomarker for monitoring pressure-perfusion-cognition relationships. Endothelial dysfunction and inflammation, microvascular disease, and mascrovascular disease affect cerebral hemodynamics and play an important role in pathohysiology and severity of multiple medical conditions, presenting as cognitive decline in the old age. Therefore, the identification of cerebrovascular vascular reactivity as a new therapeutic target is needed for prevention of cognitive decline late in life.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
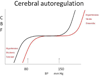

References
-
-
Pereira M, Lunet N, Azevedo A, Barros H. Differences in prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension between developing and developed countries. J Hypertens. 2009;27:963–975. Distribution and impact of hypertension worldwide.
-
-
- Rutan GH, Hermanson B, Bild DE, Kittner SJ, LaBaw F, Tell GS. Orthostatic hypotension in older adults. The Cardiovascular Health Study. CHS Collaborative Research Group. Hypertension. 1992;19:508–519. - PubMed
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C, Shaw J. IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;94:311–321. - PubMed
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365:217–223. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
