Alzheimer brain-derived tau oligomers propagate pathology from endogenous tau
- PMID: 23050084
- PMCID: PMC3463004
- DOI: 10.1038/srep00700
Alzheimer brain-derived tau oligomers propagate pathology from endogenous tau
Abstract
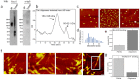
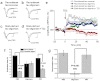
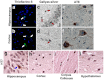
Intracerebral injection of brain extracts containing amyloid or tau aggregates in transgenic animals can induce cerebral amyloidosis and tau pathology. We extracted pure populations of tau oligomers directly from the cerebral cortex of Alzheimer disease (AD) brain. These oligomers are potent inhibitors of long term potentiation (LTP) in hippocampal brain slices and disrupt memory in wild type mice. We observed for the first time that these authentic brain-derived tau oligomers propagate abnormal tau conformation of endogenous murine tau after prolonged incubation. The conformation and hydrophobicity of tau oligomers play a critical role in the initiation and spread of tau pathology in the naïve host in a manner reminiscent of sporadic AD.
Conflict of interest statement
R. K. has patent applications on the compositions and methods related to tau oligomers and antibodies.
Figures

References
-
- Meyer-Luehmann M. et al. Exogenous induction of cerebral beta-amyloidogenesis is governed by agent and host. Science 313, 1781–1784 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

