Rearranged anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene in adult-onset papillary thyroid cancer amongst atomic bomb survivors
- PMID: 23050789
- PMCID: PMC3487115
- DOI: 10.1089/thy.2011.0511
Rearranged anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene in adult-onset papillary thyroid cancer amongst atomic bomb survivors
Abstract
Background: We previously noted that among atomic bomb survivors (ABS), the relative frequency of cases of adult papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) with chromosomal rearrangements (mainly RET/PTC) was significantly greater in those with relatively higher radiation exposure than those with lower radiation exposure. In contrast, the frequency of PTC cases with point mutations (mainly BRAF(V600E)) was significantly lower in patients with relatively higher radiation exposure than those with lower radiation exposure. We also found that among ABS, the frequency of PTC cases with no detectable gene alterations in RET, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor 1 (NTRK1), BRAF, or RAS was significantly higher in patients with relatively higher radiation exposure than those with lower radiation exposure. However, in ABS with PTC, the relationship between the presence of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene fused with other gene partners and radiation exposure has received little study. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that the relative frequency of rearranged ALK in ABS with PTC, and with no detectable gene alterations in RET, NTRK1, BRAF, or RAS, would be greater in those having relatively higher radiation exposures.
Methods: The 105 subjects in the study were drawn from the Life Span Study cohort of ABS of Hiroshima and Nagasaki who were diagnosed with PTC between 1956 and 1993. Seventy-nine were exposed (>0 mGy), and 26 were not exposed to A-bomb radiation. In the 25 ABS with PTC, and with no detectable gene alterations in RET, NTRK1, BRAF, or RAS, we examined archival, formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded PTC specimens for rearrangement of ALK using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and 5' rapid amplification of cDNA ends (5' RACE).
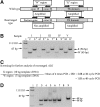
Results: We found rearranged ALK in 10 of 19 radiation-exposed PTC cases, but none among 6 patients with PTC with no radiation exposure. In addition, solid/trabecular-like architecture in PTC was closely associated with ALK rearrangements, being observed in 6 of 10 PTC cases with ALK rearrangements versus 2 of 15 cases with no ALK rearrangements. The six radiation-exposed cases of PTC harboring both ALK rearrangements and solid/trabecular-like architecture were associated with higher radiation doses and younger ages at the time of the A-bombing and at diagnosis compared to the other 19 PTC with no detectable gene alterations.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that ALK rearrangements are involved in the development of radiation-induced adult-onset PTC.
Figures


References
-
- Imaizumi M. Usa T. Tominaga T. Neriishi K. Akahoshi M. Nakashima E. Ashizawa K. Hida A. Soda M. Fujiwara S. Yamada M. Ejima E. Yokoyama N. Okubo M. Sugino K. Suzuki G. Maeda R. Nagataki S. Eguchi K. Radiation dose-relationships for thyroid nodules and autoimmune thyroid diseases in Hiroshima and Nagasaki atomic bomb survivors 55–58 years after radiation exposure. JAMA. 2006;295:1011–1022. - PubMed
-
- Kazakov VS. Demidchik EP. Astakhova LN. Thyroid cancer after Chernobyl. Nature. 1992;359:21. - PubMed
-
- Astakhova LN. Anspaugh LR. Beebe G.W. Bouville A. Drozdovitch VV. Garber V. Gavrilin YI. Khrouch VT. Kuvshinnikov AV. Kuzmenkov YN. Minenko VP. Moschik KV. Nalivko AS. Robbins J. Shemiakina EV. Shinkarev S. Tochitskaya SI. Waclawiw MA. Chernobyl-related thyroid cancer in children of Belarus: A case-control study. Radiat Res. 1998;150:349–356. - PubMed
-
- Thompson DE. Mabuchi K. Ron E. Soda M. Tokunaga M. Ochikubo S. Sugimoto S. Ikeda T. Terasaki M. Izumi S. Preston DL. Cancer incidence in atomic bomb survivors. Part II: Solid tumors, 1958–1987. Radiat Res. 1994;137:S17–S67. - PubMed
-
- Preston DL. Ron E. Tokuoka S. Funamoto S. Nishi N. Soda M. Mabuchi K. Kodama K. Solid cancer incidence in atomic bomb survivors: 1958–1998. Radiat Res. 2007;168:1–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

