Viral infections and molecular mimicry in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 23051179
- PMCID: PMC5774991
- DOI: 10.1111/apm.12011
Viral infections and molecular mimicry in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
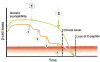
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a disease characterized by inflammation of pancreatic islets associated with autoimmunity against insulin-producing beta cells, leading to their progressive destruction. The condition constitutes a significant and worldwide problem to human health, particularly because of its rapid, but thus far unexplained, increase in incidence. Environmental factors such as viral infections are thought to account for this trend. While there is no lack of reports associating viral infections toT1D, it has proven difficult to establish which immunological processes link viral infections to disease onset or progression. One of the commonly discussed pathways is molecular mimicry, a mechanism that encompasses cross-reactive immunity against epitopes shared between viruses and beta cells. In this review, we will take a closer look at mechanistic evidence for a potential role of viruses in T1D, with a special focus on molecular mimicry.
© 2012 The Authors APMIS © 2012 APMIS.
Figures

References
-
- Barnett AH, Eff C, Leslie RD, Pyke DA. Diabetes in identical twins. A study of 200 pairs. Diabetologia. 1981;20:87–93. - PubMed
-
- Lo SS, Tun RY, Hawa M, Leslie RD. Studies of diabetic twins. Diabetes Metabo Rev. 1991;7:223–38. - PubMed
-
- Redondo MJ, Yu L, Hawa M, Mackenzie T, Pyke DA, Eisenbarth GS, et al. Heterogeneity of type I diabetes: analysis of monozygotic twins in Great Britain and the United States. Diabetologia. 2001;44:354–62. - PubMed
-
- Redondo MJ, Jeffrey J, Fain PR, Eisenbarth GS, Orban T. Concordance for islet autoimmunity among monozygotic twins. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2849–50. - PubMed
-
- Patterson CC, Dahlquist GG, Gyurus E, Green A, Soltesz G. Incidence trends for childhood type 1 diabetes in Europe during 1989-2003 and predicted new cases 2005–20: a multicentre prospective registration study. Lancet. 2009;373:2027–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

