Resiniferatoxin and tetrodotoxin induced NPY and TH immunoreactivity changes within the paracervical ganglion neurons supplying the urinary bladder
- PMID: 23054585
- PMCID: PMC3532721
- DOI: 10.1007/s12031-012-9889-z
Resiniferatoxin and tetrodotoxin induced NPY and TH immunoreactivity changes within the paracervical ganglion neurons supplying the urinary bladder
Abstract
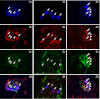
Both resiniferatoxin (RTX) and tetrodotoxin (TTX) have been reported to be effective in several urinary bladder dysfunction clinical trials. The aim of this study was to establish the effect of intravesical administration of RTX and TTX on neuropeptides Y (NPY) and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) relationship in the paracervical ganglion (PCG) neurons supplying the urinary bladder in the pig. TH is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of the amino acid L-tyrosine to dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) and is used as a marker of catecholaminergic neurons. NPY augments the vasoconstrictor effects of noradrenergic neurons, and is involved in pathophysiological processes as a neuromodulator. To identify the PCG neurons supplying urinary bladder Fast Blue (FB) was injected into the bladder wall prior to intravesical RTX or TTX administration. Consequent application of immunocytochemical methods revealed that in control group 64.08 % of FB-positive PCG neurons contain NPY and 4.25 % TH. Intravesical infusion of RTX resulted upregulation of the NPY-IR neurons to 82.97 % and TH-IR to 43.78 %. Also administration of TTX induced further increase number of TH-IR neurons to 77.49 % but induced decrease number of NPY-IR neurons to 57.45 %. Both neurotoxins affect chemical coding of the PCG neural somata supplying urinary bladder, but the effects of their action are different. This results shed light on possible involvement of RTX and TTX on curing tissue, and potentially could help us to broaden our neurourological armamentarium.
Figures
References
-
- Apostolidis A, Brady CM, Yiangou Y, Davis J, Fowler CJ, Anand P. Capsaicin receptor TRPV1 in urothelium of neurogenic human bladders and effect of intravesical resiniferatoxin. Urology. 2005;65:400–405. - PubMed
-
- Apostolidis A, Gonzales GE, Fowler CJ. Effect of intravesical resiniferatoxin (RTX) on lower urinary tract symptoms, urodynamic parameters, and quality of life of patients with urodynamic increased bladder sensation. Eur Urol. 2006;50:1299–1305. - PubMed
-
- Bossowska A, Borkowski A, Radziszewski P, Majewski M. Resiniferatoxin (RTX)- and tetrodotoxin (TTX)-induced changes in chemical coding of sensory neurons in lumbar and sacral/coccygeal dorsal root ganglia (DRG) supplying porcine urinary bladder. Pol Urol. 2008;61:1.
-
- Bossowska A, Lepiarczyk E, Radziszewski P, Borkowski A, Majewski M. C21 - botulinum toxin (BTX)- and guanethidine-induced changes at chemical coding of paracervical ganglion (PCG) neurons supplying porcine urinary bladder. Eur Urol Suppl. 2009;8:664.
-
- Burliński PJ, Gonkowski S, Całka J. Tetrodotoxin- and resiniferatoxin-induced changes in paracervical ganglion ChAT- and nNOS-IR neurons supplying the porcine urinary bladder. Acta Vet Hung. 2011;59:455–463. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

