Impact of intelligent phacoemulsification software on torsional phacoemulsification surgery
- PMID: 23055669
- PMCID: PMC3460720
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S35283
Impact of intelligent phacoemulsification software on torsional phacoemulsification surgery
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to compare phacoemulsification energy parameters during torsional phacoemulsification with or without the use of intelligent phacoemulsification (IP) software.
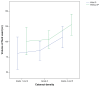
Methods: One hundred and twenty-eight eyes with nuclear grades ranging from 1 to 5 were enrolled in this randomized prospective study. Operated eyes were divided into two groups, ie, those operated on using IP software (Group 1, n = 67) and those operated on without IP software (Group 2, n = 61). The two groups were compared in terms of ultrasound energy level, ultrasound energy time, aspiration time, and amount of fluid used during surgery.
Results: Operated eyes were further grouped according to soft (grade 1 and 2, n = 37), medium (grade 3, n = 46), and hard (grade 4 and 5, n = 31) nuclear densities. Both the study and the control groups were similar in distribution of nuclear density (P > 0.05). Cumulative dissipated energy was measured as 14.06 ± 9.92 in Group 1 and 14.22 ± 10.99 in Group 2 (P = 0.92). Total ultrasound time was 49 seconds in Group 1 and 52 seconds in Group 2 (P = 0.58). Although the torsional amplitude used was similar (P = 0.86) when IP was either on (71%) or off (68.4%), aspiration time was found to be 4 minutes 17 seconds in Group 1 (P = 0.86) and 5 minutes and 17 seconds in Group 2 (P = 0.007). Total fluid used was measured as 91 cc (P = 0.86) in Group 1 and 109 cc (P = 0.02) in Group 2.
Conclusion: The new IP software did not cause a difference in ultrasound energy levels. However, the new software was found to be advantageous in regards to fluid use and aspiration time.
Keywords: Ozil; cataract surgery; cumulative dissipated energy; phacoemulsification; ultrasound energy.
Figures
References
-
- Reuschel A, Bogatsch H, Barth T, Wiedemann R. Comparison of endothelial changes and power settings between torsional and longitudinal phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010;36:1855–1861. - PubMed
-
- Rekas M, Montés-Micó R, Krix-Jachym K, Kluś A, Stankiewicz A, Ferrer-Blasco T. Comparison of torsional and longitudinal modes using phacoemulsification parameters. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35:1719–1724. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Zeng M, Liu X, Luo L, Yuan Z, Xia Y, et al. Torsional mode versus conventional ultrasound mode phacoemulsification: randomized comparative clinical study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007;33:287–292. - PubMed
-
- Davison JA. Cumulative tip travel and implied followability of longitudinal and torsional phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008;34:986–990. - PubMed
-
- Cionni RJ, Crandall AS, Felsted D. Length and frequency of intraoperative occlusive events with new torsional phacoemulsification software. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011;37:1785–1790. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources