Identification of significant pathways in gastric cancer based on protein-protein interaction networks and cluster analysis
- PMID: 23055812
- PMCID: PMC3459423
- DOI: 10.1590/S1415-47572012005000045
Identification of significant pathways in gastric cancer based on protein-protein interaction networks and cluster analysis
Abstract
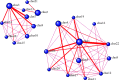
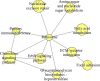
Gastric cancer is one of the most common and lethal cancers worldwide. However, despite its clinical importance, the regulatory mechanisms involved in the aggressiveness of this cancer are still poorly understood. A better understanding of the biology, genetics and molecular mechanisms of gastric cancer would be useful in developing novel targeted approaches for treating this disease. In this study we used protein-protein interaction networks and cluster analysis to comprehensively investigate the cellular pathways involved in gastric cancer. A primary immunodeficiency pathway, focal adhesion, ECM-receptor interactions and the metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 were identified as four important pathways associated with the progression of gastric cancer. The genes in these pathways, e.g., ZAP70, IGLL1, CD79A, COL6A3, COL3A1, COL1A1, CYP2C18 and CYP2C9, may be considered as potential therapeutic targets for gastric cancer.
Keywords: graph clustering; pathway crosstalk; protein-protein interaction network.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bioinformatics analysis with graph-based clustering to detect gastric cancer-related pathways.Genet Mol Res. 2012 Sep 26;11(3):3497-504. doi: 10.4238/2012.September.26.5. Genet Mol Res. 2012. PMID: 23079843
-
Prognosis genes in gastric adenocarcinoma identified by cross talk genes in disease‑related pathways.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Aug;16(2):1232-1240. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6699. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28586067 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Potential Biomarkers Associated with Prognosis in Gastric Cancer via Bioinformatics Analysis.Med Sci Monit. 2021 Feb 14;27:e929104. doi: 10.12659/MSM.929104. Med Sci Monit. 2021. PMID: 33582701 Free PMC article.
-
The Extracellular Matrix: An Accomplice in Gastric Cancer Development and Progression.Cells. 2020 Feb 8;9(2):394. doi: 10.3390/cells9020394. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32046329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of Notch signaling in gastric carcinoma: molecular pathogenesis and novel therapeutic targets.Oncotarget. 2017 May 11;8(32):53839-53853. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17809. eCollection 2017 Aug 8. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28881855 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the Association of Genetic Polymorphism of Cytochrome p450 (CYP2C9*3) in Gastric Cancer Using Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (PCR-RFLP).Cureus. 2022 Jul 25;14(7):e27220. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27220. eCollection 2022 Jul. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36035062 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor Effect of Poplar Propolis on Human Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma A431 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 25;24(23):16753. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316753. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069077 Free PMC article.
-
The modulation relationship of genomic pattern of intratumor heterogeneity and immunity microenvironment heterogeneity in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2020 Nov;20(5):233. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12096. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32968455 Free PMC article.
-
Radiogenomic signatures reveal multiscale intratumour heterogeneity associated with biological functions and survival in breast cancer.Nat Commun. 2020 Sep 25;11(1):4861. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18703-2. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32978398 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of differential network modularity in tissue specific normal and cancer protein interaction networks.J Clin Bioinforma. 2013 Oct 6;3(1):19. doi: 10.1186/2043-9113-3-19. J Clin Bioinforma. 2013. PMID: 24093757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calpe E, Codony C, Baptista MJ, Abrisqueta P, Carpio C, Purroy N, Bosch F, Crespo M. ZAP-70 enhances migration of malignant B lymphocytes toward CCL21 by inducing CCR7 expression via IgM-ERK1/2 activation. Blood. 2011;118:4401–4410. - PubMed
-
- Clements WM, Wang J, Sarnaik A, Kim OJ, MacDonald J, Fenoglio-Preiser C, Groden J, Lowy AM. β-catenin mutation is a frequent cause of Wnt pathway activation in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 2002;62:3503–3506. - PubMed
Internet Resources
-
- Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) data repository at NCBI, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/GSE2685 (November 8, 2011).
-
- R program: http://www.r-project.org/ (November 11, 2011).
-
- DPClus, http://kanaya.naist.jp/DPClus/.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

