Elevated tobramycin concentrations following endotracheal administration in a premature infant
- PMID: 23055870
- PMCID: PMC3462063
- DOI: 10.5863/1551-6776-13.2.88
Elevated tobramycin concentrations following endotracheal administration in a premature infant
Abstract
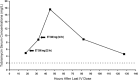
The following case report describes a 1-month-old, 34-week-gestation premature neonate who had compromised renal function. The neonate received endotracheally administered tobramycin (300 mg every 12 hours) via a PARI PLUS reusable nebulizer to treat a documented Gram-negative tracheostomy infection. The patient also received systemic tobramycin (2.5 mg/kg intravenously every 18 hours). The tobramycin serum concentration obtained 45 hours after the last intravenous dose and 11.5 hours after the second nebulized dose was 17.6 mg/L. The tobramycin nebulizations were stopped.
Keywords: endotracheal; neonate; tobramycin.
Figures
References
-
- Klastersky J, Geuning C, Mouawad E, Daneau D. Endotracheal gentamicin in bronchial infections in patients with tracheostomy. Chest. 1972;61:117–120. - PubMed
-
- Klastersky J, Huysmans E, Weerts D. Endotracheally administered gentamicin for the prevention of infections of the respiratory tract in patients with tracheostomy: A double-blind study. Chest. 1974;65:650–654. et al. - PubMed
-
- Odio W, VanLaer E, Klastersky J. Concentrations of gentamicin in bronchial secretions after intramuscular and endotracheal administration. J Clin Pharmacol. 1975;15:518–524. - PubMed
-
- Park DR. The microbiology of ventilator-associated pneumonia. Respir Care. 2005;50:742–763. - PubMed
-
- Gough PA, Jordan NS. A review of the therapeutic efficacy of aerosolized and endotracheally instilled antibiotics. Pharmacotherapy. 1982;2:367–377. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
