Clonality despite sex: the evolution of host-associated sexual neighborhoods in the pathogenic fungus Penicillium marneffei
- PMID: 23055919
- PMCID: PMC3464222
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002851
Clonality despite sex: the evolution of host-associated sexual neighborhoods in the pathogenic fungus Penicillium marneffei
Abstract
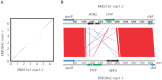
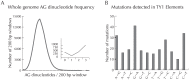
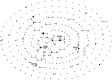
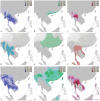
Molecular genetic approaches typically detect recombination in microbes regardless of assumed asexuality. However, genetic data have shown the AIDS-associated pathogen Penicillium marneffei to have extensive spatial genetic structure at local and regional scales, and although there has been some genetic evidence that a sexual cycle is possible, this haploid fungus is thought to be genetically, as well as morphologically, asexual in nature because of its highly clonal population structure. Here we use comparative genomics, experimental mixed-genotype infections, and population genetic data to elucidate the role of recombination in natural populations of P. marneffei. Genome wide comparisons reveal that all the genes required for meiosis are present in P. marneffei, mating type genes are arranged in a similar manner to that found in other heterothallic fungi, and there is evidence of a putatively meiosis-specific mutational process. Experiments suggest that recombination between isolates of compatible mating types may occur during mammal infection. Population genetic data from 34 isolates from bamboo rats in India, Thailand and Vietnam, and 273 isolates from humans in China, India, Thailand, and Vietnam show that recombination is most likely to occur across spatially and genetically limited distances in natural populations resulting in highly clonal population structure yet sexually reproducing populations. Predicted distributions of three different spatial genetic clusters within P. marneffei overlap with three different bamboo rat host distributions suggesting that recombination within hosts may act to maintain population barriers within P. marneffei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- de Wit R, Bouvier T (2006) ‘Everything is everywhere, but, the environment selects’; what did Baas Becking and Beijerinck really say? Environ Microbiol 8: 755–758. - PubMed
-
- Finlay BJ (2002) Global dispersal of free-living microbial eukaryote species. Science 296: 1061–1063. - PubMed
-
- Green JL, Bohannan BJM, Whitaker RJ (2008) Microbial biogeography: From taxonomy to traits. Science 320: 1039–1043. - PubMed
-
- Henk DA, Eagle CE, Brown K, Van Den Berg MA, Dyer PS, et al. (2011) Speciation despite globally overlapping distributions in Penicillium chrysogenum: the population genetics of Alexander Fleming's lucky fungus. Mol Ecol 4288–4301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

