MicroRNAs in cancers and neurodegenerative disorders
- PMID: 23056009
- PMCID: PMC3458258
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00194
MicroRNAs in cancers and neurodegenerative disorders
Abstract
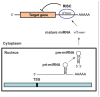
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs which function as endogenous silencers of various target genes. miRNAs are expressed in a tissue-specific manner and playing important roles in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation during mammalian development. Links between miRNAs and the initiation and progression of human diseases including cancer are becoming increasingly apparent. Recent studies have revealed that some miRNAs such as miR-9, miR-29 family, and miR-34 family are differentially expressed in Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and Huntington's disease. These miRNAs are also reported to act as tumor suppressors during human carcinogenesis. In this review, we discuss about miRNAs which are important in the molecular pathogenesis of both cancer and neurodegeneration. Cancer and neurodegenerative disorder may be influenced by common miRNA pathways that regulate differentiation, proliferation, and death of cells.
Keywords: cancer; miR-29a/29b-1; miR-34b/34c; miR-9; microRNA; neurodegenerative disorder.
References
-
- Calin G. A., Croce C. M. (2006). MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6 857–866 - PubMed
-
- Calin G. A., Sevignani C., Dumitru C. D., Hyslop T., Noch E., Yendamuri S., Shimizu M., Rattan S., Bullrich F., Negrini M., Croce C. M. (2004). Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 2999–3004 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan J. A., Krichevsky A. M., Kosik K. S. (2005). MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 65 6029–6033 - PubMed
-
- Cimmino A., Calin G. A., Fabbri M., Iorio M. V., Ferracin M., Shimizu M., Wojcik S. E., Aqeilan R. I., Zupo S., Dono M., Rassenti L., Alder H., Volinia S., Liu C. G., Kipps T. J., Negrini M., Croce C. M. (2005). miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102 13944–13949 - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources