Acute plasma biomarkers of T cell activation set-point levels and of disease progression in HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 23056251
- PMCID: PMC3462744
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046143
Acute plasma biomarkers of T cell activation set-point levels and of disease progression in HIV-1 infection
Abstract
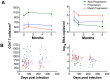
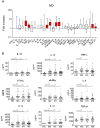
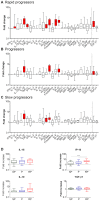
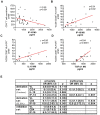
T cell activation levels, viral load and CD4(+) T cell counts at early stages of HIV-1 infection are predictive of the rate of progression towards AIDS. We evaluated whether the inflammatory profile during primary HIV-1 infection is predictive of the virological and immunological set-points and of disease progression. We quantified 28 plasma proteins during acute and post-acute HIV-1 infection in individuals with known disease progression profiles. Forty-six untreated patients, enrolled during primary HIV-1 infection, were categorized into rapid progressors, progressors and slow progressors according to their spontaneous progression profile over 42 months of follow-up. Already during primary infection, rapid progressors showed a higher number of increased plasma proteins than progressors or slow progressors. The plasma levels of TGF-β1 and IL-18 in primary HIV-1 infection were both positively associated with T cell activation level at set-point (6 months after acute infection) and together able to predict 74% of the T cell activation variation at set-point. Plasma IP-10 was positively and negatively associated with, respectively, T cell activation and CD4(+) T cell counts at set-point and capable to predict 30% of the CD4(+) T cell count variation at set-point. Moreover, plasma IP-10 levels during primary infection were predictive of rapid progression. In primary infection, IP-10 was an even better predictor of rapid disease progression than viremia or CD4(+) T cell levels at this time point. The superior predictive capacity of IP-10 was confirmed in an independent group of 88 HIV-1 infected individuals. Altogether, this study shows that the inflammatory profile in primary HIV-1 infection is associated with T cell activation levels and CD4(+) T cell counts at set-point. Plasma IP-10 levels were of strong predictive value for rapid disease progression. The data suggest IP-10 being an earlier marker of disease progression than CD4(+) T cell counts or viremia levels.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Giorgi JV, Hultin LE, McKeating JA, Johnson TD, Owens B, et al. (1999) Shorter survival in advanced human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection is more closely associated with T lymphocyte activation than with plasma virus burden or virus chemokine coreceptor usage. J Infect Dis 179: 859–870. - PubMed
-
- Shi M, Taylor JM, Fahey JL, Hoover DR, Munoz A, et al. (1997) Early levels of CD4, neopterin, and beta 2-microglobulin indicate future disease progression. J Clin Immunol 17: 43–52. - PubMed
-
- Hazenberg MD, Otto SA, van Benthem BH, Roos MT, Coutinho RA, et al. (2003) Persistent immune activation in HIV-1 infection is associated with progression to AIDS. Aids 17: 1881–1888. - PubMed
-
- Goujard C, Bonarek M, Meyer L, Bonnet F, Chaix ML, et al. (2006) CD4 cell count and HIV DNA level are independent predictors of disease progression after primary HIV type 1 infection in untreated patients. Clin Infect Dis 42: 709–715. - PubMed
-
- Deeks SG, Kitchen CM, Liu L, Guo H, Gascon R, et al. (2004) Immune activation set point during early HIV infection predicts subsequent CD4+ T-cell changes independent of viral load. Blood 104: 942–947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

