Renalase's expression and distribution in renal tissue and cells
- PMID: 23056310
- PMCID: PMC3463591
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046442
Renalase's expression and distribution in renal tissue and cells
Abstract
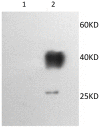
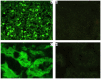
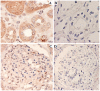
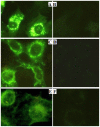
To study renalase's expression and distribution in renal tissues and cells, renalase coded DNA vaccine was constructed, and anti-renalase monoclonal antibodies were produced using DNA immunization and hybridoma technique, followed by further investigation with immunological testing and western blotting to detect the expression and distribution of renalase among the renal tissue and cells. Anti-renalase monoclonal antibodies were successfully prepared by using DNA immunization technique. Further studies with anti-renalase monoclonal antibody showed that renalase expressed in glomeruli, tubule, mesangial cells, podocytes, renal tubule epithelial cells and its cells supernatant. Renalase is wildly expressed in kidney, including glomeruli, tubule, mesangial cells, podocytes and tubule epithelial cells, and may be secreted by tubule epithelial cells primarily.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Desir GV (2008) Renalase deficiency in chronic kidney disease, and its contribution to hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 17: 181–185. - PubMed
-
- Desir GV (2007) Renalase is a novel renal hormone that regulates cardiovascular function. J Am Soc Hypertens 1: 99–103. - PubMed
-
- Xu J, Desir GV (2007) Renalase, a new renal hormone: its role in health and disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 16: 373–378. - PubMed
-
- Wang F, Wang N, Xing T, Cao Y, Xiang H (2009) The cloning and expression of renalase and the preparation of its monoclonal antibody. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ 14: 376–379.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

