Impact of cell type and epitope tagging on heterologous expression of G protein-coupled receptor: a systematic study on angiotensin type II receptor
- PMID: 23056563
- PMCID: PMC3466278
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047016
Impact of cell type and epitope tagging on heterologous expression of G protein-coupled receptor: a systematic study on angiotensin type II receptor
Abstract
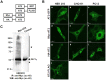
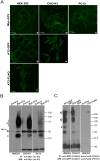
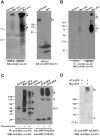
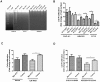
Despite heterologous expression of epitope-tagged GPCR is widely adopted for functional characterization, there is lacking of systematic analysis of the impact of expression host and epitope tag on GPCR expression. Angiotensin type II (AT2) receptor displays agonist-dependent and -independent activities, coupling to a spectrum of signaling molecules. However, consensus has not been reached on the subcellular distributions, signaling cascades and receptor-mediated actions. To examine the contributions of host cell and epitope tag on receptor expression and activity, epitope-tagged AT2 receptor variants were transiently or stably expressed in HEK293, CHO-K1 and PC12 cells. The epitope-tagged AT2 receptor variants were detected both on the cell membrane and in the perinuclear region. In transiently transfected HEK293 cells, Myc-AT2 existed predominantly as monomer. Additionally, a ladder of ubiquitinated AT2 receptor proteins was detected. By contrast, stably expressed epitope-tagged AT2 receptor variants existed as both monomer and high molecular weight complexes, and the latter was enriched in cell surface. Glycosylation promoted cell surface expression of Myc-AT2 but had no effect on AT2-GFP in HEK293 cells. In cells that stably expressed Myc-AT2, serum starvation induced apoptosis in CHO-K1 cells but not in HEK293 or PC12 cells. Instead, HEK293 and PC12 cells stably expressing Myc-AT2 exhibited partial cell cycle arrest with cells accumulating at G1 and S phases, respectively. Taken together, these results suggest that expression levels, subcellular distributions and ligand-independent constitutive activities of AT2 receptor were cell type-dependent while posttranslational processing of nascent AT2 receptor protein was modulated by epitope tag and mode of expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Type 1 angiotensin receptor (AT1-R)-mediated decrease in type 2 angiotensin receptor mRNA level is dependent on Gq and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1//2 in AT1-R-transfected PC12 cells.J Neuroendocrinol. 2008 Mar;20(3):299-308. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2008.01646.x. Epub 2008 Jan 15. J Neuroendocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18208547
-
The angiotensin II type 2 receptor causes constitutive growth of cardiomyocytes and does not antagonize angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated hypertrophy.Hypertension. 2005 Dec;46(6):1347-54. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000193504.51489.cf. Epub 2005 Nov 14. Hypertension. 2005. PMID: 16286564
-
Angiotensin AT1 and AT2 receptor heteromer expression in the hemilesioned rat model of Parkinson's disease that increases with levodopa-induced dyskinesia.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Aug 17;17(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01908-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32807174 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of angiotensin type 2 receptor over-expression on the rat mesangial cell fibrotic phenotype: effect of gender.J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2012 Jun;13(2):221-31. doi: 10.1177/1470320311432185. Epub 2012 Jan 27. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2012. PMID: 22287496
-
Role of Phe308 in the seventh transmembrane domain of the AT2 receptor in ligand binding and signaling.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Jul 9;319(4):1138-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.05.092. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15194486
Cited by
-
Melanocortin 3 receptor has a 5' exon that directs translation of apically localized protein from the second in-frame ATG.Mol Endocrinol. 2014 Sep;28(9):1547-57. doi: 10.1210/me.2014-1105. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Mol Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25051171 Free PMC article.
-
The delta opioid receptor tool box.Neuroscience. 2016 Dec 3;338:145-159. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.06.028. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Neuroscience. 2016. PMID: 27349452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation of G protein-coupled receptor antibodies differentially sensitive to conformational states.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 1;12(11):e0187306. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187306. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29091950 Free PMC article.
-
Variable Effects of C-Terminal Fusions on FLS2 Function: Not All Epitope Tags Are Created Equal.Plant Physiol. 2018 Jun;177(2):522-531. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.01700. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Plant Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29686160 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 3 (LPA3): Signaling and Phosphorylation Sites.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 12;25(12):6491. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126491. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kallal L, Benovic JL (2000) Using green fluorescent proteins to study G-protein-coupled receptor localization and trafficking. Trends Pharmacol Sci 21: 175–180. - PubMed
-
- Agbulut O, Huet A, Niederlander N, Puceat M, Menasche P, et al. (2007) Green fluorescent protein impairs actin-myosin interactions by binding to the actin-binding site of myosin. J Biol Chem 282: 10465–10471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

