Emotional states modulate the recognition potential during word processing
- PMID: 23056588
- PMCID: PMC3466240
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047083
Emotional states modulate the recognition potential during word processing
Abstract
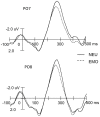
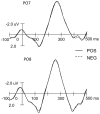
This study examined emotional modulation of word processing, showing that the recognition potential (RP), an ERP index of word recognition, could be modulated by different emotional states. In the experiment, participants were instructed to compete with pseudo-competitors, and via manipulation of the outcome of this competition, they were situated in neutral, highly positive, slightly positive, highly negative or slightly negative emotional states. They were subsequently asked to judge whether the referent of a word following a series of meaningless character segmentations was an animal or not. The emotional induction task and the word recognition task were alternated. Results showed that 1) compared with the neutral emotion condition, the peak latency of the RP under different emotional states was earlier and its mean amplitude was smaller, 2) there was no significant difference between RPs elicited under positive and negative emotional states in either the mean amplitude or latency, and 3) the RP was not affected by different degrees of positive emotional states. However, compared to slightly negative emotional states, the mean amplitude of the RP was smaller and its latency was shorter in highly negative emotional states over the left hemisphere but not over the right hemisphere. The results suggest that emotional states influence word processing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
The priming effect of emotional words on body expressions: Two ERP studies.Int J Psychophysiol. 2024 Aug;202:112370. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2024.112370. Epub 2024 May 25. Int J Psychophysiol. 2024. PMID: 38802049
-
Neuronal generator patterns at scalp elicited by lateralized aversive pictures reveal consecutive stages of motivated attention.Neuroimage. 2016 Nov 15;142:337-350. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.05.059. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Neuroimage. 2016. PMID: 27263509 Free PMC article.
-
Reward expectation regulates brain responses to task-relevant and task-irrelevant emotional words: ERP evidence.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016 Feb;11(2):191-203. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsv097. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26245838 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of valence and arousal on emotional word processing are modulated by concreteness: Behavioral and ERP evidence from a lexical decision task.Int J Psychophysiol. 2016 Dec;110:231-242. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2016.07.499. Epub 2016 Jul 16. Int J Psychophysiol. 2016. PMID: 27432482
-
Negative expectations influence behavioral and ERP responses in the subsequent recognition of expectancy-incongruent neutral events.Psychophysiology. 2020 Mar;57(3):e13492. doi: 10.1111/psyp.13492. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Psychophysiology. 2020. PMID: 31608460
Cited by
-
Individual differences in the early recognition of moral information in lexical processing: An event-related potential study.Sci Rep. 2017 May 3;7(1):1475. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01623-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28469271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dolan R J (2002) Emotion, Cognition, and Behavior. Science 298: 1191–1194. - PubMed
-
- Cacioppo JT, Gardner WL (1999) Emotion. Annu Rev Psychol 50: 191–214. - PubMed
-
- Herbert C, Kissler J, Junghofer M, Peyk P, Rockstroh B (2006) Processing of emotional adjectives: Evidence from startle EMG and ERPs. Psychophysiol 43: 197–206. - PubMed
-
- Herbert C, Junghofer M, Kissler J (2008) Event related potentials to emotional adjectives during reading. Psychophysiol 45: 487–498. - PubMed
-
- Inaba M, Nomura M, Ohira H (2005) Neural evidence of emotional valence on word recognition. Int J Psychophysiol 57: 165–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

