Limbal stem cells in review
Abstract
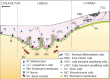
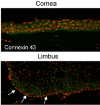
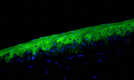
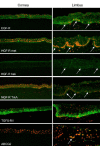
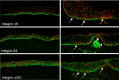
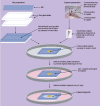
The ocular surface consists of two distinct types of epithelial cells; conjunctival and corneal. Although anatomically continuous, these epithelia comprise two distinct cell populations. Corneal stem cells are located at the limbus. The microenvironment of the limbus is important in maintaining "stemness" of the stem cells and also acts as a barrier to conjunctival epithelial cells preventing them from migration onto the corneal surface.Damage to the limbus results in varying degrees of limbal stem cell deficiency with characteristic clinical features including conjunctivalization of the cornea. Regenerative management of corneal conjunctivalization utilizing stem cells comprises of two approaches; limbal auto- or allografts by using existing stem cells and induction and regeneration of ocular tissues from embryonic stem cells. Herein, we review stem cells and limbal stem cells in particular, types of epithelial cells in the cornea, markers of corneal epithelial cells in different stages, as well as the current approach to corneal epithelial regeneration.
Keywords: Corneal; Epithelium; Limbus Corneae; Stem Cells.
Figures






References
-
- Daniels JT, Dart JK, Tuft SJ, Khaw PT. Corneal stem cells in review. Wound Repair Regen. 2001;9:483–494. - PubMed
-
- Germain L, Carrier P, Auger FA, Salesse C, Guerin SL. Can we produce a human corneal equivalent by tissue engineering? Prog Retin Eye Res. 2000;19:497–527. - PubMed
-
- Chung EH, Bukusoglu G, Zieske JD. Localization of corneal epithelial stem cells in the developing rat. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992;33:2199–2206. - PubMed
-
- Moore JE, McMullen CB, Mahon G, Adamis AP. The corneal epithelial stem cell. DNA Cell Biol. 2002;21:443–451. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
