Second messenger regulation of biofilm formation: breakthroughs in understanding c-di-GMP effector systems
- PMID: 23057745
- PMCID: PMC4936406
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101011-155705
Second messenger regulation of biofilm formation: breakthroughs in understanding c-di-GMP effector systems
Abstract
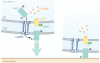
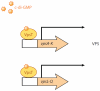
The second messenger bis-(3'-5')-cyclic dimeric guanosine monophosphate (c-di-GMP) has emerged as a broadly conserved intracellular signaling molecule. This soluble molecule is important for controlling biofilm formation, adhesion, motility, virulence, and cell morphogenesis in diverse bacterial species. But how is the typical bacterial cell able to coordinate the actions of upward of 50 proteins involved in synthesizing, degrading, and binding c-di-GMP? Understanding the specificity of c-di-GMP signaling in the context of so many enzymes involved in making, breaking, and binding the second messenger will be possible only through mechanistic studies of its output systems. Here we discuss three newly characterized c-di-GMP effector systems that are best understood in terms of molecular and structural detail. As they are conserved across many bacterial species, they likely will serve as central paradigms for c-di-GMP output systems and contribute to our understanding of how bacteria control critical aspects of their biology.
Figures
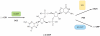

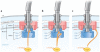
References
-
- Amikam D, Galperin MY. PilZ domain is part of the bacterial c-di-GMP binding protein. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:3–6. - PubMed
-
- Andrade MO, Alegria MC, Guzzo CR, Docena C, Rosa MC, et al. The HD-GYP domain of RpfG mediates a direct linkage between the Rpf quorum-sensing pathway and a subset of diguanylate cyclase proteins in the phytopathogen Xanthomonas axonopodis pv citri. Mol. Microbiol. 2006;62:537–51. - PubMed
-
- Barends TR, Hartmann E, Griese JJ, Beitlich T, Kirienko NV, et al. Structure and mechanism of a bacterial light-regulated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 2009;459:1015–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

