An unusual cause for recurrent chest infections
- PMID: 23060375
- PMCID: PMC4544164
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2012-006910
An unusual cause for recurrent chest infections
Abstract
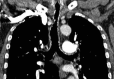
We present a case of an elderly non-smoking gentleman who, since 2005, had been admitted multiple times for recurrent episodes of shortness of breath, wheeze, cough and sputum. The patient was treated as exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and/or lower respiratory tract infections. Bronchoscopy was done which revealed multiple hard nodules in the trachea and bronchi with posterior tracheal wall sparing. Biopsies confirmed this as tracheopathia osteochondroplastica (TO). He had increasing frequency of admission due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and pseudomonas infections, which failed to clear despite intravenous, prolonged oral and nebulised antibiotics. The patient developed increasing respiratory distress and respiratory failure. The patient died peacefully in 2012. This case report highlights the typical pathological and radiological findings of TO and the pitfalls of misdiagnosing patients with recurrent chest infections as COPD.
Figures




References
-
- Chroneou A, Zias N, Gonzalez AV, et al. Tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica. An underrecognized entity? Monaldi Arch Chest Dis 2008;69:65–9. - PubMed
-
- Toth C. Tracheopathia osteoplastica. A 100-year-old mystery. Pathologe 2012;33:129–34. - PubMed
-
- Smid L, Lavrencak B, Zargi M. Larngo-tracheo-bronchopathia chondro-osteoplastica. J Laryngol Otol 1992;106:845–8. - PubMed
-
- Hempel KJ, Glaser A. Pathogenesis of chondro-osteoplastic tracheopathy. Virchows Arch 1958;331:36–50. - PubMed
-
- Bergeron D, Cormier Y, Desmeules M. Trancheobronchopathia osterochondroplastica. Am Rev Respir Dis 1976;114:803–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
