A Wii virtual activity severe thumb metacarpal injury
- PMID: 23060377
- PMCID: PMC4544152
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2012-006967
A Wii virtual activity severe thumb metacarpal injury
Abstract
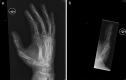
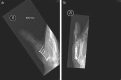
In this paper we present a case of a severe thumb bone injury sustained during simulated sporting activity using a Wii games console. Although several types of injury related to this form of physical activity have been encountered during the last few years with increasing frequency, this particular basal thumb fracture has not been reported in the literature yet. This was a complex Rolando type of fracture similar to those obtained doing the actual activity mimicked by the game. Ensuring a safe environment and adequate preparation before undertaking sport is key to prevent injury and the same principles are needed when undertaking virtual sport.
Figures
References
-
- Sparks D, Chase D, Coughlin L. Wii have a problem: a review of self-reported Wii related injuries. Inform Prim Care 2009;17:55–7. - PubMed
-
- Mandal A, Imran D, Erdmann M. Prolonged use of electronic games-a word of caution. Injury 2005;36/1:218–19. - PubMed
-
- Macgregor DM. Nintendonitis? A case report of repetitive strain injury in a child as a result of playing computer games. Scott Med J 2004;45:150. - PubMed
-
- Michael PN, Mark SC, John WS. Magnetic resonance imaging of acute ‘Wiitis’ of the upper extremity. Skeletal Radiol 2008;37:481–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical