MetaboLights: towards a new COSMOS of metabolomics data management
- PMID: 23060735
- PMCID: PMC3465651
- DOI: 10.1007/s11306-012-0462-0
MetaboLights: towards a new COSMOS of metabolomics data management
Abstract
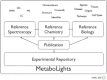
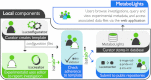
Exciting funding initiatives are emerging in Europe and the US for metabolomics data production, storage, dissemination and analysis. This is based on a rich ecosystem of resources around the world, which has been build during the past ten years, including but not limited to resources such as MassBank in Japan and the Human Metabolome Database in Canada. Now, the European Bioinformatics Institute has launched MetaboLights, a database for metabolomics experiments and the associated metadata (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/metabolights). It is the first comprehensive, cross-species, cross-platform metabolomics database maintained by one of the major open access data providers in molecular biology. In October, the European COSMOS consortium will start its work on Metabolomics data standardization, publication and dissemination workflows. The NIH in the US is establishing 6-8 metabolomics services cores as well as a national metabolomics repository. This communication reports about MetaboLights as a new resource for Metabolomics research, summarises the related developments and outlines how they may consolidate the knowledge management in this third large omics field next to proteomics and genomics.
Figures
References
-
- Fiehn O., Robertson D., Griffin J., et al. The metabolomics standards initiative (MSI) Metabolomics. 2007;3(3):175–178. doi: 10.1007/s11306-007-0070-6. - DOI
-
- O’Callaghan S., DeSouza D. P., Isaac A., Wang Q., Hodkinson L., Olshansky M., Erwin T., Appelbe B., Tull D. L., Roessner U., Bacic A., McConville M. J., Likic V. A. PyMS: A Python toolkit for processing of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) data. Application and comparative study of selected tools. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012;13(1):115. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- BB/E025080/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/I000771/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/I000933/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A090_1006/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous