Transcription factor binding at enhancers: shaping a genomic regulatory landscape in flux
- PMID: 23060900
- PMCID: PMC3460357
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00195
Transcription factor binding at enhancers: shaping a genomic regulatory landscape in flux
Abstract
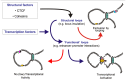
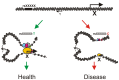
The mammalian genome is packed tightly in the nucleus of the cell. This packing is primarily facilitated by histone proteins and results in an ordered organization of the genome in chromosome territories that can be roughly divided in heterochromatic and euchromatic domains. On top of this organization several distinct gene regulatory elements on the same chromosome or other chromosomes are thought to dynamically communicate via chromatin looping. Advances in genome-wide technologies have revealed the existence of a plethora of these regulatory elements in various eukaryotic genomes. These regulatory elements are defined by particular in vitro assays as promoters, enhancers, insulators, and boundary elements. However, recent studies indicate that the in vivo distinction between these elements is often less strict. Regulatory elements are bound by a mixture of common and lineage-specific transcription factors which mediate the long-range interactions between these elements. Inappropriate modulation of the binding of these transcription factors can alter the interactions between regulatory elements, which in turn leads to aberrant gene expression with disease as an ultimate consequence. Here we discuss the bi-modal behavior of regulatory elements that act in cis (with a focus on enhancers), how their activity is modulated by transcription factor binding and the effect this has on gene regulation.
Keywords: chromatin looping; cis-regulation; enhancer; transcription; transcription factor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contribution of transposable elements and distal enhancers to evolution of human-specific features of interphase chromatin architecture in embryonic stem cells.Chromosome Res. 2018 Mar;26(1-2):61-84. doi: 10.1007/s10577-018-9571-6. Epub 2018 Jan 15. Chromosome Res. 2018. PMID: 29335803
-
Genome-Wide Mapping Targets of the Metazoan Chromatin Remodeling Factor NURF Reveals Nucleosome Remodeling at Enhancers, Core Promoters and Gene Insulators.PLoS Genet. 2016 Apr 5;12(4):e1005969. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005969. eCollection 2016 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27046080 Free PMC article.
-
Transposable elements as a potent source of diverse cis-regulatory sequences in mammalian genomes.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020 Mar 30;375(1795):20190347. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0347. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32075564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating Enhancer Function and Transcription.Annu Rev Biochem. 2020 Jun 20;89:213-234. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-011420-095916. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Annu Rev Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32197056 Review.
-
Remote control of gene transcription.Hum Mol Genet. 2005 Apr 15;14 Spec No 1:R101-11. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi104. Hum Mol Genet. 2005. PMID: 15809261 Review.
Cited by
-
Combinatorial transcription factor binding encodes cis-regulatory wiring of mouse forebrain GABAergic neurogenesis.Dev Cell. 2025 Jan 20;60(2):288-304.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.10.004. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Dev Cell. 2025. PMID: 39481376
-
Administration of genetic expression by multi-task proteins and long-range action.Front Genet. 2013 Apr 10;4:52. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2013.00052. eCollection 2013. Front Genet. 2013. PMID: 23596458 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
NXN Gene Epigenetic Changes in an Adult Neurogenesis Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Cells. 2022 Mar 22;11(7):1069. doi: 10.3390/cells11071069. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406633 Free PMC article.
-
Functional organization of the white gene enhancer in Drosophila melanogaster.Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2015;461:89-93. doi: 10.1134/S1607672915020076. Epub 2015 May 5. Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 25937222 No abstract available.
-
KDM2A/B lysine demethylases and their alternative isoforms in development and disease.Nucleus. 2018;9(1):431-441. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2018.1498707. Nucleus. 2018. PMID: 30059280 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albuisson J., Isidor B., Giraud M., Pichon O., Marsaud T., David A., et al. (2011). Identification of two novel mutations in Shh long-range regulator associated with familial pre-axial polydactyly. Clin. Genet. 79 371–377 - PubMed
-
- Alvarez M., Rhodes S. J., Bidwell J. P. (2003). Context-dependent transcription: all politics is local. Gene 313 43–57 - PubMed
-
- Amouyal M. (1991). The remote control of transcription, DNA looping and DNA compaction. Biochimie 73 1261–1268 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

