Telomere-independent functions of telomerase in nuclei, cytoplasm, and mitochondria
- PMID: 23061047
- PMCID: PMC3460319
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2012.00133
Telomere-independent functions of telomerase in nuclei, cytoplasm, and mitochondria
Abstract
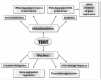
Telomerase canonical activity at telomeres prevents telomere shortening, allowing chromosome stability and cellular proliferation. To perform this task, the catalytic subunit (telomerase reverse transcriptase, TERT) of the enzyme works as a reverse transcriptase together with the telomerase RNA component (TERC), adding telomeric repeats to DNA molecule ends. Growing evidence indicates that, besides the telomeric-DNA synthesis activity, TERT has additional functions in tumor development and is involved in many different biological processes, among which cellular proliferation, gene expression regulation, and mitochondrial functionality. TERT has been shown to act independently of TERC in the Wnt-β-catenin signaling pathway, regulating the expression of Wnt target genes, which play a role in development and tumorigenesis. Moreover, TERT RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity has been found, leading to the genesis of double-stranded RNAs that act as precursor of silencing RNAs. In mitochondria, a TERT TERC-independent reverse transcriptase activity has been described that could play a role in the protection of mitochondrial integrity. In this review, we will discuss some of the extra-telomeric functions of telomerase.
Keywords: RNA interference; TERT; apoptosis; cancer; mitochondria; telomerase; telomere; transformation.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed S., Passos J. F., Birket M. J., Beckmann T., Brings S., Peters H., et al. (2008). Telomerase does not counteract telomere shortening but protects mitochondrial function under oxidative stress. J. Cell Sci. 121 1046–1053 - PubMed
-
- Barisoni L., Mokrzycki M., Sablay L., Nagata M., Yamase H., Mundel P. (2000). Podocyte cell cycle regulation and proliferation in collapsing glomerulopathies. Kidney Int. 58 137–143 - PubMed
-
- Belgiovine C., Chiodi I., Mondello C. (2008). Telomerase: cellular immortalization and neoplastic transformation. Multiple functions of a multifaceted complex. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 122 255–262 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

