Reactive metabolites in the biotransformation of molecules containing a furan ring
- PMID: 23061605
- PMCID: PMC3574180
- DOI: 10.1021/tx3003824
Reactive metabolites in the biotransformation of molecules containing a furan ring
Abstract
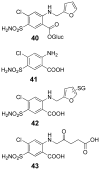
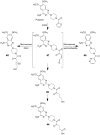
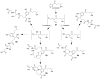
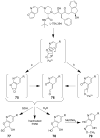
Many xenobiotics containing a furan ring are toxic and/or carcinogenic. The harmful effects of these compounds require furan ring oxidation. This reaction generates an electrophilic intermediate. Depending on the furan ring substituents, the intermediate is either an epoxide or a cis-enedione with more ring substitution favoring epoxide formation. Either intermediate reacts with cellular nucleophiles such as protein or DNA to trigger toxicities. The reactivity of the metabolite determines which cellular nucleophiles are targeted. The toxicity of a particular furan is also influenced by the presence of competing metabolic pathways or efficient detoxification routes. GSH plays an important role in modulating the harmful effects of this class of compound by reacting with the reactive metabolite. However, this may not represent a detoxification step in all cases.
Figures













Similar articles
-
Polyamines are traps for reactive intermediates in furan metabolism.Chem Res Toxicol. 2011 Nov 21;24(11):1924-36. doi: 10.1021/tx200273z. Epub 2011 Sep 12. Chem Res Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21842885 Free PMC article.
-
Degraded protein adducts of cis-2-butene-1,4-dial are urinary and hepatocyte metabolites of furan.Chem Res Toxicol. 2009 Jun;22(6):997-1007. doi: 10.1021/tx800377v. Chem Res Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 19441776 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity mediated by reactive metabolites of furans.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;136 Pt B:865-79. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981. PMID: 7344518
-
Electrophilic intermediates produced by bioactivation of furan.Drug Metab Rev. 2006;38(4):615-26. doi: 10.1080/03602530600959417. Drug Metab Rev. 2006. PMID: 17145691 Review.
-
Metabolic Activation and Hepatotoxicity of Furan-Containing Compounds.Drug Metab Dispos. 2022 May;50(5):655-670. doi: 10.1124/dmd.121.000458. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Drug Metab Dispos. 2022. PMID: 35078805 Review.
Cited by
-
Urinary metabolites of furan in waterpipe tobacco smokers compared to non-smokers in home settings in the US.Toxicol Lett. 2020 Oct 15;333:202-210. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2020.08.002. Epub 2020 Aug 16. Toxicol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32814080 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic molecules for disruption of the MYC protein-protein interface.Bioorg Med Chem. 2018 Aug 7;26(14):4234-4239. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2018.07.019. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Bioorg Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30037753 Free PMC article.
-
Reactivity of the 2-Methylfuran Phase I Metabolite 3-Acetylacrolein Toward DNA.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Nov 13;72(45):25319-25329. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c07280. Epub 2024 Nov 4. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 39494867 Free PMC article.
-
A Ligand-Based Drug Design. Discovery of 4-Trifluoromethyl-7,8-pyranocoumarin as a Selective Inhibitor of Human Cytochrome P450 1A2.J Med Chem. 2015 Aug 27;58(16):6481-93. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00494. Epub 2015 Aug 10. J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26222195 Free PMC article.
-
The status of isocyanide-based multi-component reactions in Iran (2010-2018).Mol Divers. 2021 May;25(2):1145-1210. doi: 10.1007/s11030-020-10049-7. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Mol Divers. 2021. PMID: 32072381 Review.
References
-
- Burka LT, Boyd MR. Bioactivation of Foreign Compounds. Academic Press; NY: 1985. Furans; pp. 243–257.
-
- Williams GM, Mattia A, Renwick A. Furan-substituted aliphatic hydrocarbons, alchohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and related esters, sulfides, disulfides and ethers (addendums) WHO Food Additives Series. 2009;60:481–532.
-
- Saunders RA, Griffith JR, Saalfield FE. Identification of some organic smog components based on rain water analysis. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1974;1:192–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

