Phytotracker, an information management system for easy recording and tracking of plants, seeds and plasmids
- PMID: 23062011
- PMCID: PMC3492177
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-4811-8-43
Phytotracker, an information management system for easy recording and tracking of plants, seeds and plasmids
Abstract
Background: A large number of different plant lines are produced and maintained in a typical plant research laboratory, both as seed stocks and in active growth. These collections need careful and consistent management to track and maintain them properly, and this is a particularly pressing issue in laboratories undertaking research involving genetic manipulation due to regulatory requirements. Researchers and PIs need to access these data and collections, and therefore an easy-to-use plant-oriented laboratory information management system that implements, maintains and displays the information in a simple and visual format would be of great help in both the daily work in the lab and in ensuring regulatory compliance.
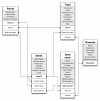
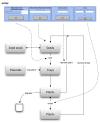
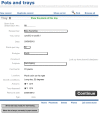
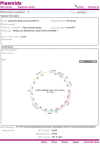
Results: Here, we introduce 'Phytotracker', a laboratory management system designed specifically to organise and track plasmids, seeds and growing plants that can be used in mixed platform environments. Phytotracker is designed with simplicity of user operation and ease of installation and management as the major factor, whilst providing tracking tools that cover the full range of activities in molecular genetics labs. It utilises the cross-platform Filemaker relational database, which allows it to be run as a stand-alone or as a server-based networked solution available across all workstations in a lab that can be internet accessible if desired. It can also be readily modified or customised further. Phytotracker provides cataloguing and search functions for plasmids, seed batches, seed stocks and plants growing in pots or trays, and allows tracking of each plant from seed sowing, through harvest to the new seed batch and can print appropriate labels at each stage. The system enters seed information as it is transferred from the previous harvest data, and allows both selfing and hybridization (crossing) to be defined and tracked. Transgenic lines can be linked to their plasmid DNA source. This ease of use and flexibility helps users to reduce their time needed to organise their plants, seeds and plasmids and to maintain laboratory continuity involving multiple workers.
Conclusion: We have developed and used Phytotracker for over five years and have found it has been an intuitive, powerful and flexible research tool in organising our plasmid, seed and plant collections requiring minimal maintenance and training for users. It has been developed in an Arabidopsis molecular genetics environment, but can be readily adapted for almost any plant laboratory research.
Figures


References
-
- Jayashree B, Reddy PT, Leeladevi Y, Crouch JH, Mahalakshmi V, Buhariwalla HK, Eshwar KE, Mace E, Folksterma R, Senthilvel S, Varshney RK, Seetha K, Rajalakshmi R, Prasanth VP, Chandra S, Swarupa L, Srikalyani P, Hoisington DA. Laboratory Information Management Software for genotyping workflows: applications in high throughput crop genotyping. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006;7:383. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-383. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Labcollector. http://labcollector.com/index.php/labcollector-add-onshtml.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

