Supramaximal elevation in B-type natriuretic peptide and its N-terminal fragment levels in anephric patients with heart failure: a case series
- PMID: 23062279
- PMCID: PMC3506524
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-6-351
Supramaximal elevation in B-type natriuretic peptide and its N-terminal fragment levels in anephric patients with heart failure: a case series
Abstract
Introduction: Little is known about the responses of natriuretic peptides to developing congestive heart failure in 'anephric' end-stage kidney disease.
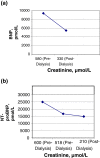
Case presentation: We present three consecutive cases of surgically-induced anephric patients in a critical care environment: a 28-year-old Caucasian woman (with congestive heart failure), a 42-year-old Caucasian woman (without congestive heart failure), and a 23-year-old Caucasian woman (without congestive heart failure). Our limited study data indicate that cut-off values advocated for B-type natriuretic peptide and its N-terminal fragment to 'rule out' congestive heart failure in two of our end-stage kidney disease patients (without congestive heart failure) are largely appropriate for anephric patients. However, our index (first) patient developed congestive heart failure accompanied by the phenomenon of massive and persistent elevation of these natriuretic levels.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that patients from the anephric subclass suffering from congestive heart failure will develop supramaximal elevation of B-type natriuretic peptide and its N-terminal fragment, implying the need for dramatically higher cut-off values with respective magnitudes of the order of 50-fold (B-type natriuretic peptide ~5780pmol/L; 20,000ng/L) to 100-fold (N-terminal fragment ~11,800pmol/L; 100,000ng/L) higher than current values used to 'rule in' congestive heart failure. Further research will be required to delineate those cut-off values. The role of our devised 'Blood Volume - B-type natriuretic peptide feedback control system' on 'anatomical' and 'functional' anephric patients led to significant mathematically-enriched arguments supporting our proposal that this model provides plausible explanations for the study findings, and the model lends support to the important hypothesis that these two groups of anephric patients inflicted with congestive heart failure should effectively have similar natriuretic response behavior.
Figures

References
-
- Anwaruddin S, Lloyd-Jones DM, Baggish A, Chen A, Krauser D, Tung R, Chae C, Januzzi JL Jr. Renal function, congestive heart failure, and amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide measurement: results from the ProBNP Investigation of Dyspnea in the Emergency Department (PRIDE) Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47(1):91–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.08.051. - DOI - PubMed
-
- McCullough PA, Duc P, Omland T, McCord J, Nowak RM, Hollander JE, Herrmann HC, Steg PG, Westheim A, Knudsen CW, Storrow AB, Abraham WT, Lamba S, Wu AH, Perez A, Clopton P, Krishnaswamy P, Kazanegra R, Maisel AS. Breathing Not Properly Multinational Study Investigators. B-type natriuretic peptide and renal function in the diagnosis of heart failure: an analysis from the Breathing Not Properly Multinational Study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41:571–579. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.2003.50118. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Goh CY, Vizzi G, De Cal M, Ronco C. Cardiorenal syndrome: a complex series of combined heart/kidney disorders. Contrib Nephrol. 2011;174:33–45. - PubMed
-
- Sarnak MJ, Levey AS, Schoolwerth AC, Coresh J, Culleton B, Hamm LL, McCullough PA, Kasiske BL, Kelepouris E, Klag MJ, Parfrey P, Pfeffer M, Raij L, Spinosa DJ, Wilson PW. Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: a statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation. 2003;108:2154–2169. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000095676.90936.80. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

