Lot-to-lot variability of test strips and accuracy assessment of systems for self-monitoring of blood glucose according to ISO 15197
- PMID: 23063033
- PMCID: PMC3570841
- DOI: 10.1177/193229681200600511
Lot-to-lot variability of test strips and accuracy assessment of systems for self-monitoring of blood glucose according to ISO 15197
Abstract
Background: Accurate and reliable blood glucose (BG) measurements require that different test strip lots of the same BG monitoring system provide comparable measurement results. Only a small number of studies addressing this question have been published.
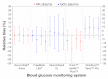
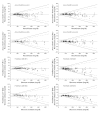
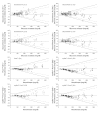
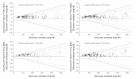
Methods: In this study, four test strip lots for each of five different BG systems [Accu-Chek® Aviva (system A), FreeStyle Lite® (system B), GlucoCheck XL (system C), Pura™/mylife™ Pura (system D), and OneTouch® Verio™ Pro (system E)] were evaluated with procedures according to DIN EN ISO 15197:2003. The BG system measurement results were compared with the manufacturer's measurement procedure (glucose oxidase or hexokinase method). Relative bias according to Bland and Altman and system accuracy according to ISO 15197 were analyzed. A BG system consists of the BG meter itself and the test strips.
Results: The maximum lot-to-lot difference between any two of the four evaluated test strip lots per BG system was 1.0% for system E, 2.1% for system A, 3.1% for system C, 6.9% for system B, and 13.0% for system D. Only two systems (systems A and B) fulfill the criteria of DIN EN ISO 15197:2003 with each test strip lot.
Conclusions: Considerable lot-to-lot variability between test strip lots of the same BG system was found. These variations add to other sources of inaccuracy with the specific BG system. Manufacturers should regularly and effectively check the accuracy of their BG meters and test strips even between different test strip lots to minimize risk of false treatment decisions.
© 2012 Diabetes Technology Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
System accuracy of blood glucose monitoring devices according to the current and proposed ISO 15197 standards.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2013 May 1;7(3):795-7. doi: 10.1177/193229681300700325. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2013. PMID: 23759413 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
In response to Teodorczyk and coauthors: System accuracy of blood glucose monitoring devices according to the current and proposed ISO 15197 standards.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2013 Nov 1;7(6):1659-60. doi: 10.1177/193229681300700632. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2013. PMID: 24351198 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(14):977–986. - PubMed
-
- Blonde L, Karter AJ. Current evidence regarding the value of self-monitored blood glucose testing. Am J Med. 2005;118(Suppl 9A):20S–26S. - PubMed
-
- IDF Clinical Guidelines Task Force Global Guideline for Type 2 Diabetes: recommendations for standard, comprehensive, and minimal care. Diabet Med. 2006;23(6):579–593. - PubMed
-
- Rodbard HW, Blonde L, Braithwaite SS, Brett EM, Cobin RH, Handelsman Y, Hellman R, Jellinger PS, Jovanovic LG, Levy P, Mechanick JI, Zangeneh F. AACE Diabetes Mellitus Clinical Practice Guidelines Task Force. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists medical guidelines for clinical practice for the management of diabetes mellitus. Endocr Pract. 2007;13(Suppl 1):1–68. - PubMed
-
- Bergenstal RM, Gavin JR., 3rd Global Consensus Conference on Glucose Monitoring Panel. The role of self-monitoring of blood glucose in the care of people with diabetes: report of a global consensus conference. Am J Med. 2005;118(Suppl 9A):1S–6S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

