Genomic and physiological characterization of the chromate-reducing, aquifer-derived Firmicute Pelosinus sp. strain HCF1
- PMID: 23064329
- PMCID: PMC3536105
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02496-12
Genomic and physiological characterization of the chromate-reducing, aquifer-derived Firmicute Pelosinus sp. strain HCF1
Abstract
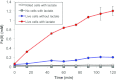
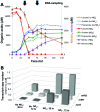
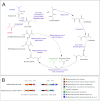
Pelosinus spp. are fermentative firmicutes that were recently reported to be prominent members of microbial communities at contaminated subsurface sites in multiple locations. Here we report metabolic characteristics and their putative genetic basis in Pelosinus sp. strain HCF1, an isolate that predominated anaerobic, Cr(VI)-reducing columns constructed with aquifer sediment. Strain HCF1 ferments lactate to propionate and acetate (the methylmalonyl-coenzyme A [CoA] pathway was identified in the genome), and its genome encodes two [NiFe]- and four [FeFe]-hydrogenases for H(2) cycling. The reduction of Cr(VI) and Fe(III) may be catalyzed by a flavoprotein with 42 to 51% sequence identity to both ChrR and FerB. This bacterium has unexpected capabilities and gene content associated with reduction of nitrogen oxides, including dissimilatory reduction of nitrate to ammonium (two copies of NrfH and NrfA were identified along with NarGHI) and a nitric oxide reductase (NorCB). In this strain, either H(2) or lactate can act as a sole electron donor for nitrate, Cr(VI), and Fe(III) reduction. Transcriptional studies demonstrated differential expression of hydrogenases and nitrate and nitrite reductases. Overall, the unexpected metabolic capabilities and gene content reported here broaden our perspective on what biogeochemical and ecological roles this species might play as a prominent member of microbial communities in subsurface environments.
Figures



References
-
- Brodie EL, Joyner DC, Faybishenko B, Conrad ME, Rios-Velazquez C, Malave J, Martinez R, Mork B, Willett A, Koenigsberg S, Herman DJ, Firestone MK, Hazen TC. 2011. Microbial community response to addition of polylactate compounds to stimulate hexavalent chromium reduction in groundwater. Chemosphere 85:660–665 - PubMed
-
- Mosher JJ, Phelps TJ, Podar M, Hurt RA, Jr, Campbell JH, Drake MM, Moberly JG, Schadt CW, Brown SD, Hazen TC, Arkin AP, Palumbo AV, Faybishenko BA, Elias DA. 2012. Microbial community succession during lactate amendment and electron acceptor limitation reveals a predominance of metal-reducing Pelosinus spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78:2082–2091 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moe WM, Stebbing RE, Rao JU, Bowman KS, Nobre MF, da Costa MS, Rainey FA. 2012. Pelosinus defluvii sp. nov., isolated from chlorinated solvent-contaminated groundwater, emended description of the genus Pelosinus and transfer of Sporotalea propionica to Pelosinus propionicus comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 62:1369–1376 - PubMed
-
- Gihring TM, Zhang G, Brandt CC, Brooks SC, Campbell JH, Carroll S, Criddle CS, Green SJ, Jardine P, Kostka JE, Lowe K, Mehlhorn TL, Overholt W, Watson DB, Yang Z, Wu WM, Schadt CW. 2011. A limited microbial consortium is responsible for extended bioreduction of uranium in a contaminated aquifer. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77:5955–5965 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schadt C, Gihring T, Carroll S, Mehlhorn T, Yang Z, Kerley M, Elias D, Watson D, Brooks S, Doktycz C, Merryfield J, Kostka J. 2012. New isolates of Geobacter, Desulforegula, Desulfovibrio, and Pelosinus and their roles in a low diversity consortia during sustained in situ reduction of U(VI), p 90 Abstr. Subsurf. Biogoechem. Res. Annu. Meet., 30 April to 2 May 2012 US Department of Energy, Washington, DC
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

