Bone disease in pediatric chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 23064662
- PMCID: PMC3594120
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-012-2324-4
Bone disease in pediatric chronic kidney disease
Abstract
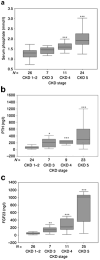
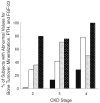
Children with long-standing chronic kidney disease (CKD) display clinical symptoms of bone disease, including bony deformities and fractures, which contribute to long-standing disability. Abnormalities in skeletal mineralization occur in a substantial proportion of this population and may contribute to chronic morbidity. Underscoring the potential contribution of parameters other than bone turnover to bone disease in CKD, a new definition for renal osteodystrophy (ROD), emphasizing the assessment of three key histologic descriptors, i.e., bone turnover (T), mineralization (M), and volume (V) (TMV), has been recommended in the assessment of all patients with CKD. Although bone biopsy is the only available method for assessing all three recommended areas of bone histology, this invasive procedure is not routinely used in any clinical setting; thus, a true understanding of the prevalence of abnormal turnover, defective mineralization, and altered bone volume throughout the course of CKD is limited. Recent data, however, have shed light on the progression of renal ROD throughout the course of CKD, including its early stages, as well as on the alterations in cell biology that accompany ROD.
Figures


References
-
- Moe S, Drueke T, Cunningham J, Goodman W, Martin K, Olgaard K, Ott S, Sprague S, Lameire N, Eknoyan G. Definition, evaluation, and classification of renal osteodystrophy: a position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Kidney Int. 2006;69:1945–1953. - PubMed
-
- Group KW. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD) Kidney Int. 2009;76:s1–s130. - PubMed
-
- Sherrard DJ, Hercz G, Pei Y, Maloney NA, Greenwood C, Manuel A, Saiphoo C, Fenton SS, Segre GV. The spectrum of bone disease in end-stage renal failure—an evolving disorder. Kidney Int. 1993;43:436–442. - PubMed
-
- Mahdavi H, Kuizon BD, Gales B, Wang HJ, Elashoff RM, Salusky IB. Sevelamer hydrochloride: an effective phosphate binder in dialyzed children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2003;18:1260–1264. - PubMed
-
- Groothoff JW, Offringa M, Van Eck-Smit BL, Gruppen MP, Van De Kar NJ, Wolff ED, Lilien MR, Davin JC, Heymans HS, Dekker FW. Severe bone disease and low bone mineral density after juvenile renal failure. Kidney Int. 2003;63:266–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

