Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm with leukemic presentation: an Italian multicenter study
- PMID: 23065521
- PMCID: PMC3561431
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2012.072645
Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm with leukemic presentation: an Italian multicenter study
Abstract
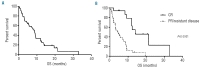
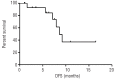
The objective of this study was to evaluate the clinical features, prognostic factors, and efficacy of treatments in patients with blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm with a leukemic presentation at onset of the disease. In order to do this, a retrospective multicenter study was performed from 2005-2011 in 28 Italian hematology divisions in which 43 cases were collected. Forty-one patients received an induction therapy, consisting of an acute myeloid leukemia-type regimen in 26 patients (60%) and acute lymphoid leukemia/lymphoma-type regimen in 15 patients (35%). Six patients (14%) underwent allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Seventeen patients (41%) achieved a complete remission: seven after acute myeloid leukemia-type treatment and 10 after an acute lymphoid leukemia/lymphoma-type regimen, with a significant advantage for acute lymphoid leukemia/lymphoma-type chemotherapy (P=0.02). Relapse occurred in six of the 17 patients (35%) who achieved complete remission, more frequently after acute lymphoid leukemia/lymphoma-type chemotherapy. The median overall survival was 8.7 months (range, 0.2-32.9). The patients treated with an acute myeloid leukemia-type regimen had an overall survival of 7.1 months (range, 0.2-19.5), whereas that of the patients receiving acute lymphoid leukemia/lymphoma-type chemotherapy was 12.3 months (range, 1-32.9) (P=0.02). The median overall survival of the allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients was 22.7 months (range, 12-32.9), and these patients had a significant survival advantage compared to the non-transplanted patients (median 7.1 months, 0.2-21.3; P=0.03). In conclusion, blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm with bone-marrow involvement is an aggressive subtype of high-risk acute leukemia. The rarity of this disease does not enable prospective clinical trials to identify the better therapeutic strategy, which, at present, is based on clinicians' experience.
Figures

Comment in
-
A combination treatment approach and cord blood stem cell transplant for blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm.Haematologica. 2013 Mar;98(3):e36. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2012.080051. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Haematologica. 2013. PMID: 23300173 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to "A combination treatment approach and cord blood stem cell transplant for blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm" and to "A low-grade B-cell lymphoma with prolymphocytic/paraimmunoblastic proliferation and IRF4 rearrangement" dendritic cell leukemia.Haematologica. 2013 Mar;98(3):e37. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2013.084582. Haematologica. 2013. PMID: 23449597 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Facchetti F, Jones D, Petrella T. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Hazzis NL, et al., eds. WHO Classification of Tumors of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon: IARC press; 2008:145-7
-
- Chaperot L, Bendriss N, Manches O, Gressin R, Maynadie M, Trimoreau F, et al. Identification of a leukemic counterpart of the plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Blood. 2001;97(10):3210-7 - PubMed
-
- Pilichowska ME, Fleming MD, Pinkus JL, Pinkus GS. CD4+/CD56+ hematodermic neoplasm (“blastic natural killer cell lymphoma”): neoplastic cells express the immature dendritic cell marker BDCA-2 and produce interferon. Am J Clin Pathol. 2007;128(3):445-53 - PubMed
-
- Bueno C, Almeida J, Lucio P, Marco J, Garcia R, de Pablos JM, et al. Incidence and characteristics of CD4(+)/HLA DRhi dendritic cell malignancies. Haematologica. 2004;89(1):58-69 - PubMed
-
- Ng AP, Lade S, Rutherford T, McCormack C, Prince HM, Westerman DA. Primary cutaneous CD4+/CD56+ hematodermic neoplasm (blastic NK-cell lymphoma): a report of five cases. Haematologica. 2006;91(1):143-4 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

