Genetic alterations of RD(INK4/ARF) enhancer in human cancer cells
- PMID: 23065809
- PMCID: PMC5557374
- DOI: 10.1002/mc.21965
Genetic alterations of RD(INK4/ARF) enhancer in human cancer cells
Abstract
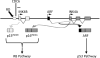
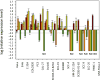
Recent identification of an enhancer element, RD(INK4/ARF) (RD), in the prominent INK4/ARF locus provides a novel mechanism to simultaneously regulate the transcription of p15(INK4B) (p15), p14(ARF) , and p16(INK4A) (p16) tumor suppressor genes. While genetic inactivation of p15, p14(ARF) , and p16 in human tumors has been extensively studied, little is known about genetic alterations of RD and its impact on p15, p14(ARF) , and p16 in human cancer. The purpose of this study was to investigate the potential existence of genetic alterations of RD in human cancer cells. DNAs extracted from 17 different cancer cell lines and 31 primary pheochromocytoma tumors were analyzed for deletion and mutation of RD using real-time PCR and direct DNA sequencing. We found that RD was deleted in human cancer cell lines and pheochromocytoma tumors at frequencies of 41.2% (7/17) and 13.0% (4/31), respectively. While some of these RD deletion events occurred along with deletions of the entire INK4/ARF locus, other RD deletion events were independent of genetic alterations in p15, p14(ARF) , and p16. Furthermore, the status of RD was poorly associated with the expression of p15, p14(ARF) , and p16 in tested cancer cell lines and tumors. This study demonstrates for the first time that deletion of the RD enhancer is a prevalent event in human cancer cells. Its implication in carcinogenesis remains to be further explored.
Keywords: CDC6; RD enhancer; genetic alteration; the INK4/ARF locus.
© 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
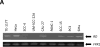
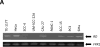

Similar articles
-
Alterations in RD(INK4/ARF) -mediated en bloc regulation of the INK4-ARF locus in human squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Mol Carcinog. 2015 Jul;54(7):532-42. doi: 10.1002/mc.22119. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Mol Carcinog. 2015. PMID: 24302590 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of RDINK4/ARF enhancer: A novel mutation to "inactivate" the INK4-ARF locus.DNA Repair (Amst). 2017 Sep;57:50-55. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.06.027. Epub 2017 Jun 24. DNA Repair (Amst). 2017. PMID: 28688373 Review.
-
Deletions of RDINK4/ARF enhancer in gastrinomas and nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.Pancreas. 2014 Oct;43(7):1009-13. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000165. Pancreas. 2014. PMID: 25003221
-
Prognostic significance of p14ARF, p15INK4b, and p16INK4a inactivation in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Jun 1;17(11):3771-82. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2393. Epub 2011 Jan 24. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21262917
-
Conspirators in a capital crime: co-deletion of p18INK4c and p16INK4a/p14ARF/p15INK4b in glioblastoma multiforme.Cancer Res. 2008 Nov 1;68(21):8657-60. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2084. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18974105 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Upregulation of MicroRNA 18b Contributes to the Development of Colorectal Cancer by Inhibiting CDKN2B.Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Oct 27;37(22):e00391-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00391-17. Print 2017 Nov 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28784723 Free PMC article.
-
Role of p14ARF and p15INK4B promoter methylation in patients with lung cancer: a systematic meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Nov 11;9:6977-6985. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S117161. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27956841 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in RD(INK4/ARF) -mediated en bloc regulation of the INK4-ARF locus in human squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Mol Carcinog. 2015 Jul;54(7):532-42. doi: 10.1002/mc.22119. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Mol Carcinog. 2015. PMID: 24302590 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that P12, a specific variant of P16(INK4A), plays a suppressive role in human pancreatic carcinogenesis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Jun 28;436(2):217-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.05.078. Epub 2013 May 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23727582 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim WY, Sharpless NE. The regulation of INK4/ARF in cancer and aging. Cell. 2006;127:265–275. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez S, Serrano M. A new mechanism of inactivation of the INK4/ARF locus. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:1382–1384. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez S, Klatt P, Delgado S, et al. Oncogenic activity of Cdc6 through repression the INK4/ARF locus. Nature. 2006;440:702–706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

