A novel EPAC-specific inhibitor suppresses pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion
- PMID: 23066090
- PMCID: PMC3533471
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.112.080689
A novel EPAC-specific inhibitor suppresses pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion
Abstract
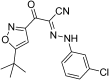
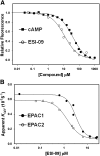
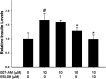
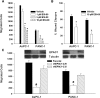
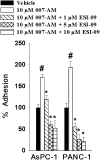
Exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (EPAC) and cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) are two intracellular receptors that mediate the effects of the prototypic second messenger cAMP. Identifying pharmacological probes for selectively modulating EPAC activity represents a significant unmet need within the research field. Herein, we report the identification and characterization of 3-(5-tert-butyl-isoxazol-3-yl)-2-[(3-chloro-phenyl)-hydrazono]-3-oxo-propionitrile (ESI-09), a novel noncyclic nucleotide EPAC antagonist that is capable of specifically blocking intracellular EPAC-mediated Rap1 activation and Akt phosphorylation, as well as EPAC-mediated insulin secretion in pancreatic β cells. Using this novel EPAC-specific inhibitor, we have probed the functional roles of overexpression of EPAC1 in pancreatic cancer cells. Our studies show that EPAC1 plays an important role in pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion, and thus represents a potential target for developing novel therapeutic strategies for pancreatic cancer.
Figures


References
-
- Arnold K, Bordoli L, Kopp J, Schwede T. (2006) The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 22:195–201 - PubMed
-
- Baljinnyam E, De Lorenzo MS, Xie LH, Iwatsubo M, Chen S, Goydos JS, Nowycky MC, Iwatsubo K. (2010) Exchange protein directly activated by cyclic AMP increases melanoma cell migration by a Ca2+-dependent mechanism. Cancer Res 70:5607–5617 - PubMed
-
- Baljinnyam E, Umemura M, De Lorenzo MS, Iwatsubo M, Chen S, Goydos JS, Iwatsubo K. (2011) Epac1 promotes melanoma metastasis via modification of heparan sulfate. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 24:680–687 - PubMed
-
- Brennesvik EO, Ktori C, Ruzzin J, Jebens E, Shepherd PR, Jensen J. (2005) Adrenaline potentiates insulin-stimulated PKB activation via cAMP and Epac: implications for cross talk between insulin and adrenaline. Cell Signal 17:1551–1559 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

