Predicting the accuracy of multiple sequence alignment algorithms by using computational intelligent techniques
- PMID: 23066102
- PMCID: PMC3592395
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks919
Predicting the accuracy of multiple sequence alignment algorithms by using computational intelligent techniques
Abstract
Multiple sequence alignments (MSAs) have become one of the most studied approaches in bioinformatics to perform other outstanding tasks such as structure prediction, biological function analysis or next-generation sequencing. However, current MSA algorithms do not always provide consistent solutions, since alignments become increasingly difficult when dealing with low similarity sequences. As widely known, these algorithms directly depend on specific features of the sequences, causing relevant influence on the alignment accuracy. Many MSA tools have been recently designed but it is not possible to know in advance which one is the most suitable for a particular set of sequences. In this work, we analyze some of the most used algorithms presented in the bibliography and their dependences on several features. A novel intelligent algorithm based on least square support vector machine is then developed to predict how accurate each alignment could be, depending on its analyzed features. This algorithm is performed with a dataset of 2180 MSAs. The proposed system first estimates the accuracy of possible alignments. The most promising methodologies are then selected in order to align each set of sequences. Since only one selected algorithm is run, the computational time is not excessively increased.
Figures
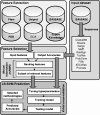
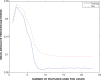
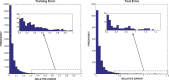
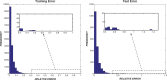
 ).
).
Similar articles
-
Optimizing multiple sequence alignments using a genetic algorithm based on three objectives: structural information, non-gaps percentage and totally conserved columns.Bioinformatics. 2013 Sep 1;29(17):2112-21. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt360. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23793754
-
Protein multiple sequence alignment benchmarking through secondary structure prediction.Bioinformatics. 2017 May 1;33(9):1331-1337. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw840. Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28093407 Free PMC article.
-
AlexSys: a knowledge-based expert system for multiple sequence alignment construction and analysis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Oct;38(19):6338-49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq526. Epub 2010 Jun 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20530533 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in features generation for membrane protein sequences: From multiple sequence alignment to pre-trained language models.Proteomics. 2023 Dec;23(23-24):e2200494. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202200494. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 37863817 Review.
-
A review on multiple sequence alignment from the perspective of genetic algorithm.Genomics. 2017 Oct;109(5-6):419-431. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2017.06.007. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28669847 Review.
References
-
- Attwood TK, Parry-Smith DJ. Introduction to Bioinformatics. Prentice Hall: Pearson Education; 2002.
-
- Pei J. Multiple protein sequence alignment. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2008;18:382–386. - PubMed
-
- Wang LS, Leebens-Mack J, Wall PK, Beckmann K, dePamphilis CW, Warnow T. The impact of multiple protein sequence alignment on phylogenetic estimation. IEEE–ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2011;8:1108–1119. - PubMed

