Impacted canines: Etiology, diagnosis, and orthodontic management
- PMID: 23066259
- PMCID: PMC3467862
- DOI: 10.4103/0975-7406.100216
Impacted canines: Etiology, diagnosis, and orthodontic management
Abstract
Impaction of maxillary and mandibular canines is a frequently encountered clinical problem, the treatment of which usually requires an interdisciplinary approach. Surgical exposure of the impacted tooth and the complex orthodontic mechanisms that are applied to align the tooth into the arch may lead to varying amounts of damage to the supporting structures of the tooth, not to mention the long treatment duration and the financial burden to the patient. Hence, it seems worthwhile to focus on the means of early diagnosis and interception of this clinical situation. In the present article, an overview of the incidence and sequelae, as well as the surgical, periodontal, and orthodontic considerations in the management of impacted canines is presented.
Keywords: Diagnosis; etiology; impacted canines; orthodontic techniques; prevention; surgical techniques.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

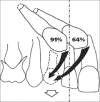
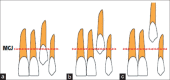
References
-
- Power SM, Short MB. An investigation into the response of palatally displaced canines to the removal of deciduous canines and an assessment of factors contributing to a favourable eruption. Br J Orthod. 1993;20:215–23. - PubMed
-
- Bishara SE. Impacted maxillary canines: A review. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1992;101:159–71. - PubMed
-
- Ericson S, Kurol J. Early treatment of palatally erupting maxillary canines by extraction of the primary canines. Eur J Orthod. 1988;10:283–95. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell L, editor. An Introduction to Orthodontics. 3rd ed. New York: Oxford University Press; 2007. pp. 147–56.

