Continuous Digital Light Processing (cDLP): Highly Accurate Additive Manufacturing of Tissue Engineered Bone Scaffolds
- PMID: 23066427
- PMCID: PMC3466612
- DOI: 10.1080/17452759.2012.673152
Continuous Digital Light Processing (cDLP): Highly Accurate Additive Manufacturing of Tissue Engineered Bone Scaffolds
Abstract
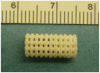
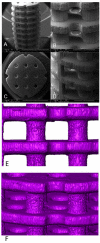
Highly accurate rendering of the external and internal geometry of bone tissue engineering scaffolds effects fit at the defect site, loading of internal pore spaces with cells, bioreactor-delivered nutrient and growth factor circulation, and scaffold resorption. It may be necessary to render resorbable polymer scaffolds with 50 μm or less accuracy to achieve these goals. This level of accuracy is available using Continuous Digital Light processing (cDLP) which utilizes a DLP(®) (Texas Instruments, Dallas, TX) chip. One such additive manufacturing device is the envisionTEC (Ferndale, MI) Perfactory(®). To use cDLP we integrate a photo-crosslinkable polymer, a photo-initiator, and a biocompatible dye. The dye attenuates light, thereby limiting the depth of polymerization. In this study we fabricated scaffolds using the well-studied resorbable polymer, poly(propylene fumarate) (PPF), titanium dioxide (TiO(2)) as a dye, Irgacure(®) 819 (BASF [Ciba], Florham Park, NJ) as an initiator, and diethyl fumarate as a solvent to control viscosity.
Figures


References
-
- Alves CM, Yang Y, Marton D, Carnes DL, Ong JL, Sylvia VL, Dean DD, Reis RL, Agrawal CM. Plasma surface modification of poly(D,L-lactic acid) as a tool to enhance protein adsorption and the attachment of different cell types. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008;87(1):59–66. - PubMed
-
- Anderson EJ, Knothe Tate ML. Design of tissue engineering scaffolds as delivery devices for mechanical and mechanically modulated signals. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(10):2525–2538. - PubMed
-
- ASTM F2792–10 . Standard terminology for additive manufacturing technologies. American Society for Testing and Materials; West Conshohocken, PA:
-
- Cheah CM, Chua CK, Leong KF, Cheong CH, Naing MW. An Automatic Algorithm for Generating Complex Polyhedral Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. 2004;10(3-4):595–610. - PubMed
-
- Dean D, Min K-J, Bond A. Computer aided design of large-format prefabricated cranial plates. J Craniofac Surg. 2003;14(6):819–832. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
