Forced sex and HIV risk in violent relationships
- PMID: 23066950
- PMCID: PMC3573255
- DOI: 10.1111/aji.12026
Forced sex and HIV risk in violent relationships
Abstract
Problem: The intersecting epidemics of gender-based violence, specifically forced sex, and HIV continue to affect women worldwide. Both in the United States and worldwide, women of African descent are disproportionately affected.
Method of study: The current literature was reviewed for inclusion based on its relevance to the intersection of forced sex and HIV risk behaviors.
Results: This brief review synthesizes research on the linkages between forced sex and behavioral risk factors for HIV infection. We explore forced sex from the perspective of the perpetrator being a current or former intimate partner, as well as the first sexual intercourse experience occurring through the use of physical force (i.e., forced sexual initiation). The review also emphasizes the importance of expanding current research to understand the physiological mechanisms linking forced sex to HIV risk.
Conclusion: The factors linking intimate partner forced sex and forced sexual initiation with HIV/AIDS are varied and complex. The review concludes with recommendations for future research in this area and implications this research could have on preventing violence and mitigating the health consequences.
© 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
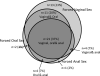
Figures

References
-
- Jewkes R. Gender Inequities Must Be Addressed in HIV Prevention. Science. 2010;329(5988):145–7. - PubMed
-
- UNAIDS World AIDS Day Report 2011. 2011
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Diagnoses of HIV Infection and AIDS in the United States and Dependent Areas, 2010. 2011;22(07/12)
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention HIV among African Americans. 2012. 2012 Mar 20;
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- L60 MD006272/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- L60MD006272/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R25MH080664/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32HD064428/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R25 MH080664/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P20MD002286/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- L60 MD003701/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- F31 MH088850/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD064428/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- L60MD003701/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DA031593/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 MD002286/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

