Increasing children's lunchtime consumption of fruit and vegetables: an evaluation of the Food Dudes programme
- PMID: 23067425
- PMCID: PMC10271278
- DOI: 10.1017/S1368980012004612
Increasing children's lunchtime consumption of fruit and vegetables: an evaluation of the Food Dudes programme
Abstract
Objectives: Although previous research has shown that the Food Dudes programme increases children's fruit and vegetable consumption at school, there has been limited evaluation of the extent to which changes are maintained in the long term. Furthermore, despite knowledge that the nutritional content of home-supplied meals is lower than that of school-supplied meals, little consideration has been given to the programme's impact on meals provided from home. The present study therefore assessed the long-term effectiveness of the Food Dudes programme for both school- and home-supplied lunches.
Design: Two cohorts of children participated, one receiving the Food Dudes intervention and a matched control group who did not receive any intervention. Consumption of fruit and vegetables was assessed pre-intervention, then at 3 and 12 months post-intervention. Consumption was measured across five consecutive days in each school using weighed intake (school-provided meals) and digital photography (home-provided meals).
Setting: Fifteen primary schools, six intervention (n 1282) and seven control schools (n 1151).
Subjects: Participants were children aged 4-11 years.
Results: A significant increase in the consumption of fruit and vegetables was found at 3 months for children in the intervention schools, but only for those eating school-supplied lunches. However, increases were not maintained at 12 months.
Conclusions: The Food Dudes programme has a limited effect in producing even short-term changes in children's fruit and vegetable consumption at lunchtime. Further development work is required to ensure the short- and long-term effectiveness of interventions promoting fruit and vegetable consumption in children such as the Food Dudes programme.
Figures

 ), 3-month follow-up (
), 3-month follow-up ( ) and 12-month follow-up (
) and 12-month follow-up ( ); primary-school children aged 4–11 years, Food Dudes programme, West Midlands, UK. Values are means with 95 % confidence intervals represented by vertical bars
); primary-school children aged 4–11 years, Food Dudes programme, West Midlands, UK. Values are means with 95 % confidence intervals represented by vertical bars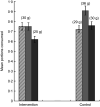
 ), 3-month follow-up (
), 3-month follow-up ( ) and 12-month follow-up (
) and 12-month follow-up ( ); primary-school children aged 4–11 years, Food Dudes programme, West Midlands, UK. Values are means with 95 % confidence intervals represented by vertical bars
); primary-school children aged 4–11 years, Food Dudes programme, West Midlands, UK. Values are means with 95 % confidence intervals represented by vertical barsComment in
-
Reply to 'evaluation of the food Dudes programme by Upton et al.'.Public Health Nutr. 2013 Aug;16(8):1523. doi: 10.1017/S1368980013000670. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Public Health Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23518062 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Children's fruit and vegetable intake, programme evaluation.Public Health Nutr. 2013 Aug;16(8):1522-3. doi: 10.1017/S1368980013000694. Epub 2013 Apr 2. Public Health Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23547566 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

