Cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2)-selective N-aryl-oxadiazolyl-propionamides: synthesis, radiolabelling, molecular modelling and biological evaluation
- PMID: 23067874
- PMCID: PMC3598492
- DOI: 10.1186/2191-2858-2-32
Cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2)-selective N-aryl-oxadiazolyl-propionamides: synthesis, radiolabelling, molecular modelling and biological evaluation
Abstract
Background: The endocannabinoid system is involved in many physiological and pathological processes. Two receptors (cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) and type 2 (CB2)) are known so far. Many unwanted psychotic side effects of inhibitors of this system can be addressed to the interaction with CB1. While CB1 is one of the most abundant neuroreceptors, CB2 is expressed in the brain only at very low levels. Thus, highly potent and selective compounds for CB2 are desired. N-aryl-((hetero)aromatic)-oxadiazolyl-propionamides represent a promising class of such selective ligands for the human CB2. Here, a library of various derivatives is studied for suitable routes for labelling with 18F. Such 18F-labelled compounds can then be employed as CB2-selective radiotracers for molecular imaging studies employing positron emission tomography (PET).
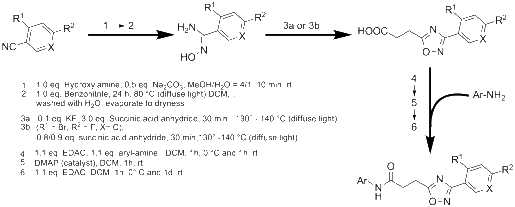
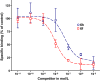
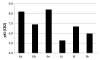
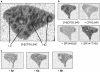
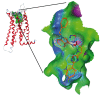
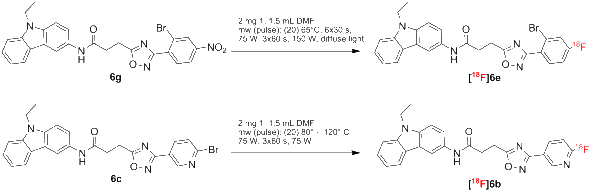
Results: By varying the N-arylamide substructure, we explored the binding pocket of the human CB2 receptor and identified 9-ethyl-9H-carbazole amide as the group with optimal size. Radioligand replacement experiments revealed that the modification of the (hetero)aromatic moiety in 3-position of the 1,2,4-oxadiazoles shows only moderate impact on affinity to CB2 but high impact on selectivity towards CB2 with respect to CB1. Further, we could show by autoradiography studies that the most promising compounds bind selectively on CB2 receptors in mouse spleen tissue. Molecular docking studies based on a novel three-dimensional structural model of the human CB2 receptor in its activated form indicate that the compounds bind with the N-arylamide substructure in the binding pocket. 18F labelling at the (hetero)aromatic moiety at the opposite site of the compounds via radiochemistry was carried out.
Conclusions: The synthesized CB2-selective compounds have high affinity towards CB2 and good selectivity against CB1. The introduction of labelling groups at the (hetero)aromatic moiety shows only moderate impact on CB2 affinity, indicating the introduction of potential labelling groups at this position as a promising approach to develop CB2-selective ligands suitable for molecular imaging with PET. The high affinity for human CB2 and selectivity against human CB1 of the herein presented compounds renders them as suitable candidates for molecular imaging studies.
Figures
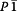


Similar articles
-
Radiofluorination and biological evaluation of N-aryl-oxadiazolyl-propionamides as potential radioligands for PET imaging of cannabinoid CB2 receptors.Org Med Chem Lett. 2013 Sep 24;3(1):11. doi: 10.1186/2191-2858-3-11. Org Med Chem Lett. 2013. PMID: 24063584 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Thiophene-Based Cannabinoid Receptor Type 2 Radiotracers for PET Imaging.Front Neurosci. 2016 Jul 27;10:350. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00350. eCollection 2016. Front Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27512365 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Highly Affine and Selective Fluorinated Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptor Ligands.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2017 Apr 28;8(5):566-571. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.7b00129. eCollection 2017 May 11. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2017. PMID: 28523112 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptor ligand specificity and the development of CB2-selective agonists.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(14):1428-43. doi: 10.2174/092986708784567716. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18537620 Review.
-
Behavioral effects of cannabinoid agents in animals.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1999;13(3):243-81. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v13.i3.20. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1999. PMID: 10803637 Review.
Cited by
-
Positron emission tomography of type 2 cannabinoid receptors for detecting inflammation in the central nervous system.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019 Mar;40(3):351-357. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0035-5. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019. PMID: 29921889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of (18)F-labeled radiotracers for neuroreceptor imaging with positron emission tomography.Neurosci Bull. 2014 Oct;30(5):777-811. doi: 10.1007/s12264-014-1460-6. Epub 2014 Aug 29. Neurosci Bull. 2014. PMID: 25172118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small Molecules from Nature Targeting G-Protein Coupled Cannabinoid Receptors: Potential Leads for Drug Discovery and Development.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:238482. doi: 10.1155/2015/238482. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26664449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis, Biodistribution and In vitro Evaluation of Brain Permeable High Affinity Type 2 Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists [11C]MA2 and [18F]MA3.Front Neurosci. 2016 Sep 22;10:431. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00431. eCollection 2016. Front Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27713686 Free PMC article.
-
Development of cannabinoid receptor (CB 2 R) ligands for application in PET studies - where to attach the radiolabel?J Cheminform. 2014 Mar 11;6(Suppl 1):O9. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-6-S1-O9. eCollection 2014 Mar. J Cheminform. 2014. PMID: 24765132 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Fowler CJ, Rojo ML, Rodriguez-Gaztelumendi A. Modulation of the endocannabinoid system: neuroprotection or neurotoxicity? Exp Neurol. 2010;224(1):37–47. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda LA, Lolait SJ, Brownstein MJ, Young AC, Bonner TI. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature. 1990;346(6284):561–564. - PubMed
-
- Alger B. Retrograde signaling in the regulation of synaptic transmission: focus on endocannabinoids. Prog Neurobiol. 2002;68(4):247–286. - PubMed
-
- Munro S, Thomas KL, Abu-Shaar M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature. 1993;365(6441):61–65. - PubMed
-
- Stella N. Cannabinoid signaling in glial cells. Glia. 2004;48(4):267–277. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

