Establishment of a Shigella sonnei human challenge model in Thailand
- PMID: 23069701
- PMCID: PMC3732056
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.09.061
Establishment of a Shigella sonnei human challenge model in Thailand
Abstract
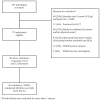
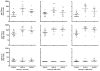
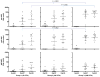
In order to establish a human challenge model of Shigella related disease for vaccine testing, a dose-escalating inpatient trial was performed. Three groups of 12 healthy adult volunteers were orally challenged with 93,440 and 1680 CFU of Shigella sonnei strain 53G. Subjects were admitted to the Vaccine Trial Centre (VTC) at Mahidol University in Bangkok, Thailand. The primary purpose of this study was to identify the dose of S. sonnei 53G required to elicit clinical disease in at least 70% of Thai adult subjects. At the highest dose of 1680 CFU, the attack rate was 75%, while at the two lower doses, the attack rate was approximately 50%. This human challenge model, which is the first of its kind in an endemic region, will provide an opportunity for S. sonnei vaccine evaluation in endemic populations.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Diarrhoeal Diseases: Shigellosis. Initiative for Vaccine Research (IVR) 2009 Feb; [cited; Available from: http://www.who.int/vaccineresearch/diseases/diarrhoeal/en/index6.html#di...]
-
- Kuo CY, Su LH, Perera J, Carlos C, Tan BH, Kumarasinghe G, et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Shigella isolates in eight Asian countries, 2001–2004. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2008 Apr;41(2):107–11. - PubMed
-
- Hill Gaston JS, Lillicrap MS. Arthritis associated with enteric infection. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2003 Apr;17(2):219–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

