The intersection between DNA damage response and cell death pathways
- PMID: 23070009
- PMCID: PMC3754840
The intersection between DNA damage response and cell death pathways
Abstract
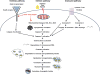
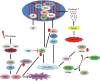
Apoptosis is a finely regulated process that serves to determine the fate of cells in response to various stresses. One such stress is DNA damage, which not only can signal repair processes but is also intimately involved in regulating cell fate. In this review we examine the relationship between the DNA damage/repair response in cell survival and apoptosis following insults to the DNA. Elucidating these pathways and the crosstalk between them is of great importance, as they eventually contribute to the etiology of human disease such as cancer and may play key roles in determining therapeutic response. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled "Apoptosis: Four Decades Later".
Figures
Similar articles
-
The p53 protein and its molecular network: modelling a missing link between DNA damage and cell fate.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1844(1 Pt B):232-47. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.09.019. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24113167 Review.
-
Cell Fate Regulation upon DNA Damage: p53 Serine 46 Kinases Pave the Cell Death Road.Bioessays. 2019 Dec;41(12):e1900127. doi: 10.1002/bies.201900127. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Bioessays. 2019. PMID: 31621101 Review.
-
Decision making of the p53 network: death by integration.J Theor Biol. 2011 Feb 21;271(1):205-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2010.11.041. Epub 2010 Dec 3. J Theor Biol. 2011. PMID: 21130774 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting synthetic lethal interactions between DNA damage signaling, checkpoint control, and p53 for targeted cancer therapy.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012;110:289-314. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387665-2.00011-0. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012. PMID: 22749150 Review.
-
ATR-Chk2 signaling in p53 activation and DNA damage response during cisplatin-induced apoptosis.J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 7;283(10):6572-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707568200. Epub 2007 Dec 27. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18162465
Cited by
-
p53 Affects PGC1α Stability Through AKT/GSK-3β to Enhance Cisplatin Sensitivity in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 21;10:1252. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01252. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32974127 Free PMC article.
-
A time-resolved experimental-mathematical model for predicting the response of glioma cells to single-dose radiation therapy.Integr Biol (Camb). 2021 Jul 8;13(7):167-183. doi: 10.1093/intbio/zyab010. Integr Biol (Camb). 2021. PMID: 34060613 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 promotes survival following exposure to ionizing radiation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt B):268-274. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.04.035. Epub 2015 May 12. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25975985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-24 Inhibits Lung Cancer Growth by Suppressing GLI1 and Inducing DNA Damage.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 27;11(12):1879. doi: 10.3390/cancers11121879. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31783569 Free PMC article.
-
MUC1: a novel metabolic master regulator.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Apr;1845(2):126-35. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2014.01.001. Epub 2014 Jan 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24418575 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
