Global processing training to improve visuospatial memory deficits after right-brain stroke
- PMID: 23070314
- PMCID: PMC3589919
- DOI: 10.1093/arclin/acs089
Global processing training to improve visuospatial memory deficits after right-brain stroke
Abstract
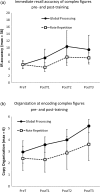
Visuospatial stimuli are normally perceived from the global structure to local details. A right-brain stroke often disrupts this perceptual organization, resulting in piecemeal encoding and thus poor visuospatial memory. Using a randomized controlled design, the present study examined whether promoting the global-to-local encoding improves retrieval accuracy in right-brain-damaged stroke survivors with visuospatial memory deficits. Eleven participants received a single session of the Global Processing Training (global-to-local encoding) or the Rote Repetition Training (no encoding strategy) to learn the Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure. The result demonstrated that the Global Processing Training significantly improved visuospatial memory deficits after a right-brain stroke. On the other hand, rote practice without a step-by-step guidance limited the degree of memory improvement. The treatment effect was observed both immediately after the training procedure and 24 h post-training. Overall, the present findings are consistent with the long-standing principle in cognitive rehabilitation that an effective treatment is based on specific training aimed at improving specific neurocognitive deficits. Importantly, visuospatial memory deficits after a right-brain stroke may improve with treatments that promote global processing at encoding.
Figures





References
-
- Akshoomoff N. A., Feroleto C. C., Doyle R. E., Stiles J. The impact of early unilateral brain injury on perceptual organization and visual memory. Neuropsychologia. 2002;40(5):539–561. doi:10.1016/s0028-3932(01)00129-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barrett A. M., Beversdorf D. Q., Crucian G. P., Heilman K. M. Neglect after right hemisphere stroke—A smaller floodlight for distributed attention. Neurology. 1998;51(4):972–978. - PubMed
-
- Binder L. M. Constructional strategies on complex figure drawings after unilateral brain damage. Journal of Clinical Neuropsychology. 1982;4(1):51–58. - PubMed
-
- Bliokas V. V., Taylor J. E., Leung J., Deane F. P. Neuropsychological assessment of fitness to drive following acquired cognitive impairment. Brain Injury. 2011;25(5):471–487. doi:10.3109/02699052.2011.559609. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bornstein R. F., Dagostino P. R. Stimulus-recognition and the mere exposure effect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1992;63(4):545–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

