Intraoperative fluid management in open gastrointestinal surgery: goal-directed versus restrictive
- PMID: 23070341
- PMCID: PMC3460017
- DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2012(10)06
Intraoperative fluid management in open gastrointestinal surgery: goal-directed versus restrictive
Abstract
Objective: The optimal strategy for fluid management during gastrointestinal surgery remains unclear. Minimizing the variation in arterial pulse pressure, which is induced by mechanical ventilation, is a potential strategy to improve postoperative outcomes. We tested this hypothesis in a prospective, randomized study with lactated Ringer's solution and 6% hydroxyethyl starch solution.
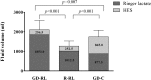
Method: A total of 60 patients who were undergoing gastrointestinal surgery were randomized into a restrictive lactated Ringer's group (n = 20), a goal-directed lactated Ringer's group (n = 20) and a goal-directed hydroxyethyl starch group (n = 20). The goal-directed fluid treatment was guided by pulse pressure variation, which was recorded during surgery using a simple manual method with a Datex Ohmeda S/5 Monitor and minimized to 11% or less by volume loading with either lactated Ringer's solution or 6% hydroxyethyl starch solution (130/0.4). The postoperative flatus time, the length of hospital stay and the incidence of complications were recorded as endpoints.
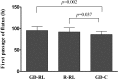
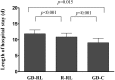
Results: The goal-directed lactated Ringer's group received the greatest amount of total operative fluid compared with the two other groups. The flatus time and the length of hospital stay in the goal-directed hydroxyethyl starch group were shorter than those in the goal-directed lactated Ringer's group and the restrictive lactated Ringer's group. No significant differences were found in the postoperative complications among the three groups.
Conclusion: Monitoring and minimizing pulse pressure variation by 6% hydroxyethyl starch solution (130/0.4) loading during gastrointestinal surgery improves postoperative outcomes and decreases the discharge time of patients who are graded American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status I/II.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Brandstrup B, Tønnesen H, Beier-Holgersen R, Hjortsø E, Ørding H, Lindorff-Larsen K, et al. Effects of intravenous fluid restriction on postoperative complications: comparison of two perioperative fluid regimens: a randomized assessor-blinded multicenter trial. Ann Surg. 2003;238(5):641–8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- MacKay G, Fearon K, McConnachie A, Serpell MG, Molloy RG, O'Dwyer PJ. Randomized clinical trial of the effect of postoperative intravenous fluid restriction on recovery after elective colorectal surgery. Br J Surg. 2006;93(12):1469–74. - PubMed
-
- Gobindram A, Gowrie-Mohan S. Major elective gastrointestinal surgery: does fluid restriction improve outcome. Br J Hosp Med (Lond) 2007;68(3):168. - PubMed
-
- Futier E, Constantin JM, Petit A, Chanques G, Kwiatkowski F, Flamein R, et al. Conservative vs restrictive individualized goal-directed fluid replacement strategy in major abdominal surgery: A prospective randomized trial. Arch Surg. 2010;145(12):1193–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources