Enthesitis-related arthritis is associated with higher pain intensity and poorer health status in comparison with other categories of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance Registry
- PMID: 23070991
- PMCID: PMC3513507
- DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.120642
Enthesitis-related arthritis is associated with higher pain intensity and poorer health status in comparison with other categories of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance Registry
Abstract
Objective: To assess the relative effect of clinical factors and medications on pain intensity, physical function, and health status in juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA).
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cross-sectional study of data from children with JIA enrolled in the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA) Registry. We tested whether clinical characteristics of JIA were associated with pain intensity, physical function, and health status using multivariable linear and ordinal logistic regression.
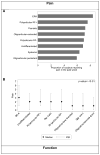
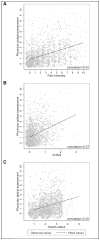
Results: During the study period, 2571 subjects with JIA enrolled in the CARRA Registry. Ratings of pain intensity, physical function, and health status differed significantly between JIA categories. In comparison to other categories of JIA, subjects with enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA) reported worse pain and function. In multivariable analyses, higher active joint count and current use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAID), biologics, or corticosteroids were associated with worse scores on all patient-reported measures. ERA and older age were significantly associated with higher pain intensity and poorer health status. Systemic JIA and uveitis were significantly associated with worse health status. Enthesitis, sacroiliac tenderness, and NSAID use were independently associated with increased pain intensity in ERA. The correlation was low between physician global assessment of disease activity and patient-reported pain intensity, physical function, and health status.
Conclusion: Significant differences in pain intensity, physical function, and health status exist among JIA categories. These results suggest that current treatments may not be equally effective for particular disease characteristics more common in specific JIA categories, such as enthesitis or sacroiliac tenderness in ERA.
Figures


References
-
- Bowyer S, Roettcher P. Pediatric rheumatology clinic populations in the United States: results of a 3 year survey. Pediatric Rheumatology Database Research Group. J Rheumatol. 1996;23(11):1968–74. - PubMed
-
- Manners PJ, Diepeveen DA. Prevalence of juvenile chronic arthritis in a population of 12-year-old children in urban Australia. Pediatrics. 1996;98(1):84–90. - PubMed
-
- Ostlie IL, Aasland A, Johansson I, Flato B, Moller A. A longitudinal follow-up study of physical and psychosocial health in young adults with chronic childhood arthritis. Clinical and experimental rheumatology. 2009;27(6):1039–46. - PubMed
-
- Packham JC, Hall MA, Pimm TJ. Long-term follow-up of 246 adults with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: predictive factors for mood and pain. Rheumatology. 2002;41(12):1444–9. - PubMed
-
- Peterson LS, Mason T, Nelson AM, O’Fallon WM, Gabriel SE. Psychosocial outcomes and health status of adults who have had juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: a controlled, population-based study. Arthritis and rheumatism. 1997;40(12):2235–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
