Fragmented QRS: What Is The Meaning?
- PMID: 23071383
- PMCID: PMC3443879
- DOI: 10.1016/s0972-6292(16)30544-7
Fragmented QRS: What Is The Meaning?
Abstract
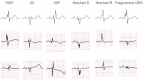
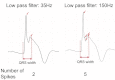
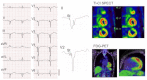
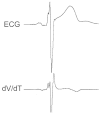
Fragmented QRS (fQRS) is a convenient marker of myocardial scar evaluated by 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) recording. fQRS is defined as additional spikes within the QRS complex. In patients with CAD, fQRS was associated with myocardial scar detected by single photon emission tomography and was a predictor of cardiac events. fQRS was also a predictor of mortality and arrhythmic events in patients with reduced left ventricular function. The usefulness of fQRS for detecting myocardial scar and for identifying high-risk patients has been expanded to various cardiac diseases, such as cardiac sarcoidosis, arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, acute coronary syndrome, Brugada syndrome, and acquired long QT syndrome. fQRS can be applied to patients with wide QRS complexes and is associated with myocardial scar and prognosis. Myocardial scar detected by fQRS is associated with subsequent ventricular dysfunction and heart failure and is a substrate for reentrant ventricular tachyarrhythmias.
Keywords: cardiac event; cardiovascular implantable electronic device (CIED); fragmented QRS; myocardial scar.
Figures



References
-
- Surawicz B, et al. Chou's electrocardiography in clinical practice. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2008.
-
- Varriale P, et al. The RSR' complex not related to right bundle branch block: diagnostic value as a sign of myocardial infarction scar. Am Heart J . 1992;123:369. - PubMed
-
- Das MK, et al. Significance of a fragmented QRS complex versus a Q wave in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation . 2006;113:2495. - PubMed
-
- Das MK, et al. Fragmented wide QRS on a 12-lead ECG: a sign of myocardial scar and poor prognosis. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol . 2008;1:258. - PubMed
-
- Das MK, et al. Fragmented QRS on a 12-lead ECG: a predictor of mortality and cardiac events in patients with coronary artery disease. Heart Rhythm . 2007;4:1385. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
