Degradable copolymer based on amphiphilic N-octyl-N-quatenary chitosan and low-molecular weight polyethylenimine for gene delivery
- PMID: 23071395
- PMCID: PMC3469101
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S36179
Degradable copolymer based on amphiphilic N-octyl-N-quatenary chitosan and low-molecular weight polyethylenimine for gene delivery
Abstract
Background: Chitosan shows particularly high biocompatibility and fairly low cytotoxicity. However, chitosan is insoluble at physiological pH. Moreover, it lacks charge, so shows poor transfection. In order to develop a new type of gene vector with high transfection efficiency and low cytotoxicity, amphiphilic chitosan was synthesized and linked with low-molecular weight polyethylenimine (PEI).
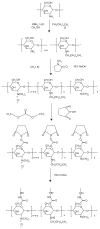
Methods: We first synthesized amphiphilic chitosan - N-octyl-N-quatenary chitosan (OTMCS), then prepared degradable PEI derivates by cross-linking low-molecular weight PEI with amphiphilic chitosan to produce a new polymeric gene vector (OTMCS-PEI). The new gene vector was characterized by various physicochemical methods. We also determined its cytotoxicity and gene transfecton efficiency in vitro and in vivo.
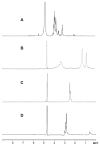
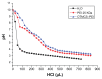
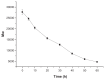
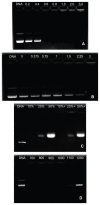
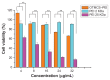
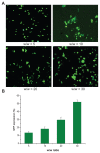
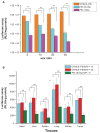
Results: The vector showed controlled degradation. It was very stable and showed excellent buffering capacity. The particle sizes of the OTMCS-PEI/DNA complexes were around 150-200 nm with proper zeta potentials from 10 mV to 30 mV. The polymer could protect plasmid DNA from being digested by DNase I at a concentration of 2.25 U DNase I/μg DNA. Furthermore, they were resistant to dissociation induced by 50% fetal bovine serum and 1100 μg/mL sodium heparin. OTMCS-PEI revealed lower cytotoxicity, even at higher doses. Compared with PEI 25 KDa, the OTMCS-PEI/DNA complexes also showed higher transfection efficiency in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: OTMCS-PEI was a potential candidate as a safe and efficient gene vector for gene therapy.
Keywords: cytotoxicity; nonviral gene vector; polyethylenimine; transfection efficiency.
Figures

References
-
- Morille M, Passirani C, Vonarbourg A, Clavreul A, Benoit JP. Progress in developing cationic vectors for non-viral systemic gene therapy against cancer. Biomaterials. 2008;29(24–25):3477–3496. - PubMed
-
- Danielsen S, Strand S, de Lange Davies C, Stokke BT. Glycosaminoglycan destabilization of DNA-chitosan polyplexes for gene delivery depends on chitosan chain length and GAG properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1721(1–3):44–54. - PubMed
-
- Verma IM, Somia N. Gene therapy – promises, problems and prospects. Nature. 1997;389(6648):239–242. - PubMed
-
- Peng M, Liu W, Yang G, et al. Investigation of the degradation mechanism of cross-linked polyethyleneimine by NMR spectroscopy. Polym Degrad Stab. 2008;93(2):476–482.
-
- Guo Q, Shi S, Wang X, et al. Synthesis of a novel biodegradable poly(ester amine) (PEAs) copolymer based on low-molecular-weight polyethyleneimine for gene delivery. Int J Pharm. 2009;379(1):82–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

