Choline kinase alpha and hexokinase-2 protein expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: association with survival
- PMID: 23071593
- PMCID: PMC3465336
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046591
Choline kinase alpha and hexokinase-2 protein expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: association with survival
Abstract
Purpose: Hexokinase-2 (HK2) and more recently choline kinase alpha (CKA) expression has been correlated with clinical outcomes in several major cancers. This study examines the protein expression of HK2 and CKA in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in association with patient survival and other clinicopathologic parameters.
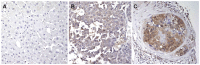
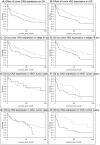
Methods: Immunohistochemical analysis for HK2 and CKA expression was performed on a tissue microarray of 157 HCC tumor samples. Results were analyzed in relation to clinicopathologic data from Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End-Results Program registries. Mortality rates were assessed by Kaplan-Meier estimates and compared using log-rank tests. Predictors of overall survival were assessed using proportional hazards regression.
Results: Immunohistochemical expression of HK2 and CKA was detected in 71 (45%) and 55 (35%) tumor samples, respectively. Differences in tumor HK2 expression were associated with tumor grade (p = 0.008) and cancer stage (p = 0.001), while CKA expression differed significantly only across cancer stage (p = 0.048). Increased mortality was associated with tumor HK2 expression (p = 0.003) as well as CKA expression (p = 0.03) with hazard ratios of 1.86 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.23-2.83) and 1.59 (95% CI 1.04-2.41), respectively. Similar effects on overall survival were noted in a subset analysis of early stage (I and II) HCC. Tumor HK2 expression, but not CKA expression, remained a significant predictor of survival in multivariable analyses.
Conclusion: HK2 and CKA expression may have biologic and prognostic significance in HCC, with tumor HK2 expression being a potential independent predictor of survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bray F, Ren JS, Masuyer E, Ferlay J (2012) Global estimates of cancer prevalence for 27 sites in the adult population in 2008. Int J Cancer - PubMed
-
- Gillies RJ, Gatenby RA (2007) Adaptive landscapes and emergent phenotypes: why do cancers have high glycolysis? J Bioenerg Biomembr 39: 251–257. - PubMed
-
- Mathupala SP, Rempel A, Pedersen PL (1997) Aberrant glycolytic metabolism of cancer cells: a remarkable coordination of genetic, transcriptional, post-translational, and mutational events that lead to a critical role for type II hexokinase. J Bioenerg Biomembr 29: 339–343. - PubMed
-
- Teefey SA, Hildeboldt CC, Dehdashti F, Siegel BA, Peters MG, et al. (2003) Detection of primary hepatic malignancy in liver transplant candidates: prospective comparison of CT, MR imaging, US, and PET. Radiology 226: 533–542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

