Plaque rupture complications in murine atherosclerotic vein grafts can be prevented by TIMP-1 overexpression
- PMID: 23071737
- PMCID: PMC3469549
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047134
Plaque rupture complications in murine atherosclerotic vein grafts can be prevented by TIMP-1 overexpression
Abstract
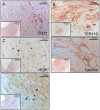
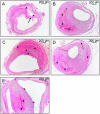
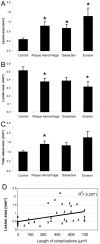
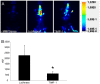
The current study describes the incidence and phenotype of plaque rupture complications in murine vein grafts. Since matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are highly involved in atherosclerotic plaque vulnerability and plaque rupture, we hypothesized that this model can be validated by overexpression of the MMP inhibitor TIMP-1. First we studied 47 vein grafts in hypercholesterolemic ApoE3*Leiden mice for the incidence of plaque complications. In 79% of these grafts, extensive lesions with plaque rupture complications like dissections, intraplaque hemorrhages or erosions with intramural thrombi were found. Next, in vivo Near-InfraRed-Fluorescence imaging demonstrated that electroporation mediated TIMP-1-overexpression reduced local MMP activity in vein grafts by 73% (p<0.01). This led to a 40% reduction in lesion-size after 28d (p = 0.01) and a more stable lesion phenotype with significant more smooth muscle cells (135%), collagen (47%) and significant less macrophages (44%) and fibrin (55%) than controls. More importantly, lesions in the TIMP-1 group showed a 90% reduction of plaque complications (10/18 of control mice showed plaque complications versus 1/18 in TIMP-1 treated mice). Murine vein grafts are a relevant spontaneous model to study plaque stability and subsequent hemorrhagic complications, resulting in plaque instability. Moreover, inhibition of MMPs by TIMP-1-overexpression resulted in decreased plaque progression, increased stabilization and decreased plaque rupture complications in murine vein grafts.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential effects of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 and TIMP-2 on atherosclerosis and monocyte/macrophage invasion.Cardiovasc Res. 2016 Feb 1;109(2):318-30. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvv268. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Cardiovasc Res. 2016. PMID: 26645981 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo suppression of vein graft disease by nonviral, electroporation-mediated, gene transfer of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 linked to the amino terminal fragment of urokinase (TIMP-1.ATF), a cell-surface directed matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor.J Vasc Surg. 2010 Feb;51(2):429-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2009.09.026. Epub 2009 Dec 24. J Vasc Surg. 2010. PMID: 20036101
-
Suppression of atherosclerotic plaque progression and instability by tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2: involvement of macrophage migration and apoptosis.Circulation. 2006 May 23;113(20):2435-44. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.613281. Epub 2006 May 15. Circulation. 2006. PMID: 16702468
-
Metalloproteinase production from macrophages - a perfect storm leading to atherosclerotic plaque rupture and myocardial infarction.Exp Physiol. 2016 Nov 1;101(11):1327-1337. doi: 10.1113/EP085567. Epub 2016 May 5. Exp Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26969796 Review.
-
Matrix metalloproteinases: influence on smooth muscle cells and atherosclerotic plaque stability.Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2007 Mar;5(2):265-82. doi: 10.1586/14779072.5.2.265. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2007. PMID: 17338671 Review.
Cited by
-
Interfering in the ALK1 Pathway Results in Macrophage-Driven Outward Remodeling of Murine Vein Grafts.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Feb 3;8:784980. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.784980. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35187106 Free PMC article.
-
bFGF blockade reduces intraplaque angiogenesis and macrophage infiltration in atherosclerotic vein graft lesions in ApoE3*Leiden mice.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 29;10(1):15968. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72992-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32994514 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of Intra-plaque Hemorrhage for the Development of High-Risk Vulnerable Plaque: Current Understanding from Basic to Clinical Points of View.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 27;24(17):13298. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713298. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biliverdin Reductase B Is a Plasma Biomarker for Intraplaque Hemorrhage and a Predictor of Ischemic Stroke in Patients with Symptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis.Biomolecules. 2023 May 24;13(6):882. doi: 10.3390/biom13060882. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37371462 Free PMC article.
-
Atorvastatin pleiotropically decreases intraplaque angiogenesis and intraplaque haemorrhage by inhibiting ANGPT2 release and VE-Cadherin internalization.Angiogenesis. 2021 Aug;24(3):567-581. doi: 10.1007/s10456-021-09767-9. Epub 2021 Feb 7. Angiogenesis. 2021. PMID: 33550461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Virmani R, Burke AP, Kolodgie FD, Farb A (2002) Vulnerable plaque: the pathology of unstable coronary lesions. J Interv Cardiol 15: 439–446. - PubMed
-
- Hansson GK, Robertson AK, Soderberg-Naucler C (2006) Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Pathol 1: 297–329. - PubMed
-
- Kolodgie FD, Gold HK, Burke AP, Fowler DR, Kruth HS, et al. (2003) Intraplaque hemorrhage and progression of coronary atheroma. N Engl J Med 349: 2316–2325. - PubMed
-
- van Lammeren GW, Pasterkamp G, de Vries JP, Bosch L, de Haan JJ, et al. (2012) Platelets enter atherosclerotic plaque via intraplaque microvascular leakage and intraplaque hemorrhage: A histopathological study in carotid plaques. Atherosclerosis 222: 355–359. - PubMed
-
- Shah PK (1998) Role of inflammation and metalloproteinases in plaque disruption and thrombosis. Vasc Med 3: 199–206. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

