T2-signal of ulnar nerve branches at the wrist in guyon's canal syndrome
- PMID: 23071777
- PMCID: PMC3468548
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047295
T2-signal of ulnar nerve branches at the wrist in guyon's canal syndrome
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate T2-signal of high-resolution MRI in distal ulnar nerve branches at the wrist as diagnostic sign of guyon's-canal-syndrome (GCS).
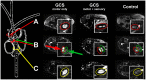
Materials and methods: 11 GCS patients confirmed by clinical/electrophysiological findings, and 20 wrists from 11 asymptomatic volunteers were prospectively included to undergo the following protocol: axial T2-weighted-fat-suppressed and T1-weighted-turbo-spin-echo-sequences (3T-MR-scanner, Magnetom/Verio/Siemens). Patients were examined in prone position with the arm extended and wrist placed in an 8-channel surface-array-coil. Nerve T2-signal was evaluated as contrast-to-noise-ratios (CNR) from proximal-to-distal in ulnar nerve trunk, its superficial/sensory and deep/motor branch. Distal motor-nerve-conduction (distal-motor-latency (dml)) to first dorsal-interosseus (IOD I) and abductor digiti minimi muscles was correlated with T2-signal. Approval by the institutional review-board and written informed consent was given by all participants.
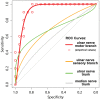
Results: In GCS, mean nerve T2-signal was strongly increased within the deep/motor branch (11.7±4.8 vs.controls:-5.3±2.4;p = 0.001) but clearly less and not significantly increased in ulnar nerve trunk (6.8±6.4vs.-7.4±2.5;p = 0.07) and superficial/sensory branch (-2.1±4.9vs.-9.7±2.9;p = 0.08). Median nerve T2-signal did not differ between patients and controls (-9.8±2.5vs.-6.7±4.2;p = 0.45). T2-signal of deep/motor branch correlated strongly with motor-conduction-velocity to IOD I in non-linear fashion (R(2) = -0.8;p<0.001). ROC-analysis revealed increased nerve T2-signal of the deep/motor branch to be a sign of excellent diagnostic performance (area-under-the-curve 0.94, 95% CI: 0.85-1.00; specificity 90%, sensitivity 89.5%).
Conclusions: Nerve T2-signal increase of distal ulnar nerve branches and in particular of the deep/motor branch is highly accurate for the diagnostic determination of GCS. Furthermore, for the first time it was found in nerve entrapment injury that T2-signal strongly correlates with electrical-conduction-velocity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
The ulnar tunnel at the wrist (Guyon's canal): normal MR anatomy and variants.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992 May;158(5):1081-5. doi: 10.2214/ajr.158.5.1566671. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992. PMID: 1566671
-
MR anatomy and pathology of the ulnar nerve involving the cubital tunnel and Guyon's canal.Clin Imaging. 2016 Mar-Apr;40(2):263-74. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2015.11.008. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Clin Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26995584 Review.
-
[Compression of the deep branch of ulnar nerve at the wrist].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 1999 Jul;13(4):225-6. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 1999. PMID: 12080804 Chinese.
-
Anomalous flexor digiti minimi brevis in Guyon's canal.Clin Anat. 2003 Jul;16(4):340-3. doi: 10.1002/ca.10087. Clin Anat. 2003. PMID: 12794919
-
Syndrome of canal of Guyon - definition, diagnosis, treatment and complication.Folia Med Cracov. 2015;55(1):17-23. Folia Med Cracov. 2015. PMID: 26774628 Review.
Cited by
-
MR Neurography: Diagnostic Imaging in the PNS.Clin Neuroradiol. 2015 Oct;25 Suppl 2:283-9. doi: 10.1007/s00062-015-0412-0. Epub 2015 Jun 13. Clin Neuroradiol. 2015. PMID: 26070607
-
A scoping review to map evidence regarding key domains and questions in the management of non-traumatic wrist disorders.Hand Ther. 2024 Mar;29(1):3-20. doi: 10.1177/17589983231219595. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Hand Ther. 2024. PMID: 38425437 Free PMC article.
-
Guyon Canal Syndrome: lack of management in a case of unresolved handlebar palsy.J Can Chiropr Assoc. 2014 Dec;58(4):413-20. J Can Chiropr Assoc. 2014. PMID: 25550666 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Resonance Neurography for Evaluation of Peripheral Nerves.J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj. 2021 May 14;16(1):e17-e23. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1729176. eCollection 2021 Jan. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj. 2021. PMID: 34007307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MR neurography in ulnar neuropathy as surrogate parameter for the presence of disseminated neuropathy.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49742. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049742. Epub 2012 Nov 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23166762 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilbourn AJ (2005) Upper limb neuropathies: Long thoracic, suprascapular, axillary, musculocutaneous, radial, ulnar, and medial antebrachial cutaneus, in peripheral neuropathy, Dyck PJ, Thomas PK (Editor); Philadelphia.
-
- Subin GD, Mallon WJ, Urbaniak JR (1989) Diagnosis of ganglion in Guyon’s canal by magnetic resonance imaging. J Hand Surg Am 14(4): 640–643. - PubMed
-
- Andreisek G, Crook DW, Burg D, Marincek B, Weishaupt D (2006) Peripheral neuropathies of the median, radial, and ulnar nerves: MR imaging features. Radiographics 26(5): 1267–1287. - PubMed
-
- Bui-Mansfield LT, Williamson M, Wheeler DT, Johnstone F (2002) Guyon’s canal lipoma causing ulnar neuropathy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 178(6): 1458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

