Oroxylin-A rescues LPS-induced acute lung injury via regulation of NF-κB signaling pathway in rodents
- PMID: 23071799
- PMCID: PMC3468516
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047403
Oroxylin-A rescues LPS-induced acute lung injury via regulation of NF-κB signaling pathway in rodents
Abstract
Background and purpose: Successful drug treatment for sepsis-related acute lung injury (ALI) remains a major clinical problem. This study was designed to assess the beneficial effects of post-treatment of oroxylin A (OroA), a flavonoid, in ameliorating lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced lung inflammation and fatality.
Experimental approach: Rats were injected with LPS (10 mg/kg, iv) to induce ALI, and OroA was given (15 mg/kg, iv) 1 hr or 6 hrs after LPS challenge. Twenty four hrs after LPS challenge, biochemical changes in the blood and lung tissues, and morphological/histological alterations in the lung associated with inflammation and injury were examined. Therapeutic effect of OroA was assessed by measuring the survival rate in endotoxemic mice.
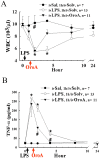
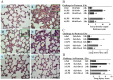
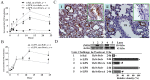
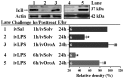
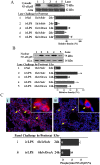
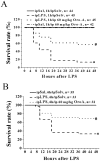
Key results: LPS (10 mg/kg, iv) significantly altered WBC counts, elevated plasma tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and nitric oxide (NO), increased pulmonary edema, thickened alveolar septa, and decreased survival rate. These changes were ameliorated by OroA (15 mg/kg, iv) administered 1 hr or 6 hrs after LPS challenge. This post-treatment also significantly attenuated LPS-induced activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and the release of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) in lung tissues. Furthermore, post-treatment with OroA (60 mg/kg, ip) administered 1 hr or 6 hrs after LPS challenge in mice significantly increased survival rate.
Conclusion and implication: OroA administered after induction of ALI by LPS significantly prevent and revere lung tissues injuries with increased survival rate. Positive post-treatment effects of OroA suggest that OroA is a potentially useful candidate for managing lung inflammation in LPS-induced endotoxemia and septic shock.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Induction of endothelium-dependent constriction of mesenteric arteries in endotoxemic hypotensive shock.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Apr;173(7):1179-95. doi: 10.1111/bph.13415. Epub 2016 Mar 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26694894 Free PMC article.
-
Kegan Liyan oral liquid ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through inhibition of TLR4-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway and MMP-9 expression.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Jun 20;186:91-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.03.057. Epub 2016 Mar 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27036629
-
Cavidine Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury via NF-κB Signaling Pathway in vivo and in vitro.Inflammation. 2017 Aug;40(4):1111-1122. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0553-1. Inflammation. 2017. PMID: 28365871
-
Tetrahydroberberrubine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by down-regulating MAPK, AKT, and NF-κB signaling pathways.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Aug;82:489-97. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.05.025. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27470389
-
[Effect of growth hormone on acute lung injury].Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2005 Sep;17(9):523-6. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2005. PMID: 16146594 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Oroxylin A Inhibits Allergic Airway Inflammation in Ovalbumin (OVA)-Induced Asthma Murine Model.Inflammation. 2016 Apr;39(2):867-72. doi: 10.1007/s10753-016-0317-3. Inflammation. 2016. PMID: 26895180
-
Euphorbia cuneata Represses LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice via its Antioxidative and Anti-inflammatory Activities.Plants (Basel). 2020 Nov 21;9(11):1620. doi: 10.3390/plants9111620. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33233453 Free PMC article.
-
Lonicera japonica Thunb extract ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury associated with luteolin-mediated suppression of NF-κB signaling pathway.J Inflamm (Lond). 2023 Dec 19;20(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12950-023-00372-9. J Inflamm (Lond). 2023. PMID: 38115057 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effects of oroxylin A on endothelial protein C receptor shedding in vitro and in vivo.BMB Rep. 2014 Jun;47(6):336-41. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2014.47.6.198. BMB Rep. 2014. PMID: 24286327 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of endotoxin-induced airway epithelial cell injury by a novel family of pyrrol derivates.Lab Invest. 2016 Jun;96(6):632-40. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2016.46. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Lab Invest. 2016. PMID: 26999659
References
-
- Dreyfuss D, Ricard JD (2005) Acute lung injury and bacterial infection. Clin Chest Med 26: 105–112. - PubMed
-
- Baumgarten G, Knuefermann P, Wrigge H, Putensen C, Stapel H, et al. (2006) Role of Toll-like receptor 4 for the pathogenesis of acute lung injury in Gram-negative sepsis. Eur J Anaesthesiol 23: 1041–1048. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y, Xu J, Zhou C, Wu Z, Zhong S, et al. (2005) Characterization of cytokine/chemokine profiles of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 171: 850–857. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

